Injection waterproofing methods. Injection waterproofing: works, materials, application features Wall waterproofing by injection
MOSCOW ADVANCED DEVELOPMENT COMPLEX
OFFICE OF EXTRA-BUDGETARY CITY DEVELOPMENT PLANNING
GENERAL PLAN DEVELOPMENT DEPARTMENT
NIIMOSSTROY
DEPARTMENTAL
BUILDING STANDARDS
INSTRUCTIONS
BY DEVICE TECHNOLOGY
WATERPROOFING AND REINFORCEMENT
WALLS, FOUNDATIONS, BASES
POLYMER HYDROPHOBIZING COMPOSITIONS
VSN 64-97
MOSCOW 1997
"Instructions on the technology of waterproofing and strengthening walls, foundations, bases with polymer water-repellent compositions" was developed by NIIMosstroy (Ph.D. B.V. Lyapidevsky, Ph.D. A.F. Lander, senior researcher T. A. Kleiman).
When using this instruction, you should take into account the approved changes to the standards and specifications for materials used for waterproofing and strengthening walls, foundations, bases with polymer water-repellent compounds.
|
Complex for perspective development of Moscow |
Departmental building codes |
VSN 64-97 |
|
|
Instructions on the technology of waterproofing and strengthening walls, foundations, bases with polymer waterproofing compounds |
Introduced for the first time |
||
|
Office of Extra-Budgetary City Development Planning |
|||
|
General Plan Development Department |
1. GENERAL PROVISIONS
1.2. When performing the work specified in., It is necessary to comply with the requirements of SNiP 3.04.01-87 "Insulation and finishing coatings" and this instruction.
1.3. Polymer compositions proposed for waterproofing and strengthening structures made of brick, stone, concrete are compositions based on water-repellent silicon compounds.
1.4. Compounds intended for waterproofing and strengthening the structure of walls and foundations must be checked for compliance with the technical requirements specified in this manual.
1.5. Polymer compositions are delivered to construction sites ready for use.
1.6. Before starting work on waterproofing and strengthening structures, preparatory work must be completed.
1.7. When performing waterproofing works with polymer and polymer-cement compositions, it is necessary to comply with the requirements of SNiP III-4-80 * "Safety in construction" and this manual.
Fig. 1.1. Water absorption mechanism diagram
Liquid water absorption:
1 - rainwater; 2 - filtration water; 3 - rising moisture;
Water absorption in the form of water vapor:
4 - capillary condensation; 5 - hygroscopic water absorption; 6 - condensation
Work is permitted under the following conditions:
Outside air temperature must not be lower than + 5 ° С;
On the outside, the walls must be frostbitten by at least half of their thickness, which is achieved by keeping at a stable round-the-clock temperature of + 8 ° C for 5 consecutive days.
It is forbidden to perform works on covering waterproofing:
In hot weather when the air temperature in the shade is + 27 ° C and with direct exposure to sunlight;
During rain and immediately after rain on a surface that has not absorbed water;
When the wind speed exceeds 10 m / s.
Waterproofing of internal surfaces is allowed to be done indoors at a temperature not lower than 10 ° C and a relative humidity of not more than 80%.
2. TECHNOLOGY OF SURFACE PREPARATION FOR WORK ON WATERPROOFING AND STRENGTHENING OF STRUCTURES
2.1. Before starting work on waterproofing and strengthening the structures of parts of buildings and structures using injection and cover methods, it is necessary:
Carefully inspect the surface of the insulated structures;
Clean up all defective places (cracks, potholes, places not tied with mortar);
The surface to be treated must be clean, durable, free from residues of fuel oil, tar, cement mortar, oil and grease stains, rubber paste, drips, etc .;
If possible, the surface should be scraped or sandblasted;
Surfaces with absorbent properties must be evenly and abundantly moistened with water, avoiding the formation of puddles;
Damaged places (chips, shells, cracks, etc.) are rubbed with polymer-cement mortar from a dry mixture of at least 75 grade, sealed with Asoplast-MC binder emulsion. (Asoplast-MC - a synthetic emulsion based on butodiene and styrene - gives the solidified solution increased adhesion, increases elasticity and resistance to soaking, reduces water permeability, increases chemical resistance).
2.2. In the case of immediate waterproofing of damp areas of surfaces, places of leakage and seepage of water in basements, mines, etc. FIKS-10s sealing cement is used.
2.3. If it is necessary to install horizontal waterproofing in the outer walls of the building, it is necessary to provide access for the installation of injectors and injection along the entire perimeter of the building (outside and inside).
2.4. Roots and cracks in walls and ceilings should be carried out with a polymer-cement composition using a dry mixture with Asoplast-MC and subsequent leveling.
The joints of dissimilar materials must be glued with gauze on a 50% plasticized polyvinyl acetate (containing dibutyl phthalate GOST 18992-80) dispersion diluted with water 2: 1 or Uniflex-B glue.
The gauze should be carefully smoothed out, not have folds, bulges and, after the adhesive layer has dried, should not peel off the surface.
3. TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR INJECTION WATERPROOFING MATERIALS
3.1. Application area:
To stop capillary absorption by creating a horizontal barrier when renovating old buildings;
To eliminate voids and shells;
To eliminate leaks in concrete, if there are various types of fasteners (anchors, consoles, protruding supports, sleeves, etc.);
For embedding sinuses in underground structures filled with rubble, pieces of concrete, construction waste or lumpy soil;
For pumping the mixture during the construction of tunnels in fractured rocky soils behind the tunnel shell to fill the free space;
In case of poor-quality monolithing of the joints of prefabricated structures;
In those structures where the concrete has not been sufficiently compacted and there are separate gravel layers and loose working joints;
In case of violations of brick and rubble masonry, which occur with uneven precipitation of the foundation, in the absence of proper dressing of the seams and poor-quality filling;
To fill voids to prevent metal corrosion, eliminate water seepage;
In order to impart solidity to the structure and increase its strength;
For filling pores with porous concrete structure;
In the presence of deep cracks, spread throughout the entire thickness of the structure.
3.2. Requirements for injectable formulations.
The composition must meet the following requirements:
Possess a waterproofing property to stop capillary suction;
Be resistant to the action of water-soluble salts;
Be resistant to aggressive substances;
Have good adhesion to masonry or concrete;
The pressure taken should not compromise the strength of the structure and cause any deformation.
3.3. Compositions used for injection waterproofing (polymer).
3.3.1. Injection composition GUI-412e:
It is a hydrophobic and strengthening solution consisting of a mixture of silicic acid esters with solvents with dilution and hydrophobic - based on GKZh-11e with a solvent and dilution - two-component for injection hydrophobization;
Designed for conservation building materials, structural strengthening and volumetric hydrophobization of inorganic porous materials, as well as for external and internal work (injection waterproofing);
Prepared at the workplace in accordance with TU 2312-008-04000633-96;
Low toxicity and fire hazard before impregnation;
Storage: in tightly closed glass containers in accordance with GOST 9980.1-86 * (shelf life 1 year);
Transportation at a temperature not higher than + 30 ° С;
Consumption for injection treatment for 1 borehole with 2-fold filling - 1 liter.
3.3.2. Injection composition "Aquafin-F" by "Schomburg":
Ready-to-use solution for silicatization based on hydrophobic silicon compounds. When interacting with lime, it forms insoluble chemical compounds that stop capillary suction;
Designed to stop capillary absorption when renovating old buildings;
Hydrophobizes and narrows or bridges the capillary structure in concrete and masonry;
Does not cause corrosion of reinforcing steel;
Technical data: base - silicon compounds, liquid; color - transparent; specific gravity - 1.2 g / cm 3;
Storage: in a warm room in closed containers. Shelf life 1 year;
The consumption is calculated based on the absorbency of the wall, according to the processing of a test hole.
For injection, it is necessary to arrange boreholes with a length of at least 2/3 of the wall thickness;
When processing walls with a thickness of more than 1 m, as well as in the corners of buildings, boreholes should be placed on both sides.
3.3.3. Injection composition "Aquafin-SMK":
Silicone microemulsion concentrate prepared on the basis of silanes and oligomeric siloxanes;
It is used for the device of horizontal waterproofing - a barrier of rising capillary moisture;
Technical data: base - silane / siloxane; color - transparent; specific gravity - 0.95 g / cm 3. Shelf life 9 months, store in a warm room;
Consumption: 1.5 - 2 kg of concentrate per 1 m 2 of the cross-sectional area of \u200b\u200bthe wall;
Does not contain solvents, odorless, non-flammable, harmless to health.
3.4. Compositions used for injection insulation (polymer-cement).
3.4.1. Fast-setting sealing compound (BUS):
Aluminate-silicate non-toxic binder;
Properties:
self-sealing;
intensive expansion;
watertightness in a stamped state;
ease of clumping and good coining.
Technical data: base - alumina expanding cement, Portland cement, alumina cement, chrysotile asbestos; color - gray;
The water-cement ratio of the cement paste is 0.28 - 0.32;
Waterproof - in a day it should be waterproof;
2) injections without overpressure for solutions based on silicon compounds.
Injection holes should be drilled at intervals of not more than 15 cm with a diameter of 30 mm and at an angle of 45 ° to 30 °. The borehole length should be 5 - 8 cm less than the wall thickness.
Masonry with large cavities, hollow bricks, cracks or open seams of more than 5 mm should be filled with BUSS or Asokret-BM materials before injection work. (.).
Before impregnation, drill cuttings should be removed from the holes.
When working with Aquafin-F material, boreholes should be filled with a 0.1% solution of lime water before impregnation. The impregnation time is at least 24 hours.
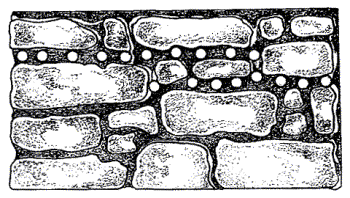
Fig. 3.1. Drilling holes in stone structures

Fig. 3.2. Basement waterproofing scheme

Fig. 3.3. Basement waterproofing scheme at the facility

Fig. 3.4. Basement waterproofing scheme

Fig. 3.5. Sealing scheme of individual leaking injection sites
Then the boreholes are filled with BUSS or Asokret-BM material.
3.5.2. The technology for strengthening the underground and aboveground parts of buildings and structures with polymer-cement compositions by the injection method:
the process of injecting a polymer-cement mixture consists of three operations:
1) preparation of wells in the body of the structure for setting injection pipes in them.
2) installation and termination of pipes.
3) injection of the mixture.
The preparation consists in clearing and expanding the place where it is supposed to install pipes with a diameter of 19 - 25 mm.
This removes weak slurry and unconsolidated gravel.
The number of prepared wells is set by the working scheme depending on the size and distribution of the defect.
The borehole depth is drilled in such a way that the pipe goes into it up to 50 - 70 mm at a certain angle, ensuring good fluid flow into the defective area.
Cleaning of shells and expansion of cracks is carried out hand tool (with a scarpel, bolt, etc.). The prepared place is washed ().
When installing the pipes, it is necessary to ensure that they accurately hit a crack or a sink that goes deep into the structure ().
Injection pipes are sealed with cement mortar of 1: 3 composition with a cone draft of 2 ... 3 cm. If the sink or crack is very large compared to the pipe, then tow soaked with liquid glass is placed around it, which is tightly coined.
The end of the tube should protrude from the body of the structure by 50 ... 100 mm to attach the hose to it.
The sealed tubes are kept for some time in order for the solution to gain the required strength ().
The cement mixture is prepared from cement grade 400 with a composition of 1: 1.5 (1 part of cement and 1.5 parts of water by volume). The mixture is prepared at the workplace in metal barrels with a capacity of 40 - 60 liters, thoroughly mixed for 2 - 3 minutes, filtered through a metal mesh, and then enters the pump. BUSS or Asokret is diluted with water.

Fig. 3.6. Installing injection pipes on a crack and pumping the solution with a pump
The injection is usually carried out by 2 people.
Through the installed pipes or directly into the borehole under a pressure of 0.2 - 2.0 MPa, injection compositions are injected "to failure".
Maintaining the ultimate pressure in this state for 5 - 10 minutes.
After partial curing of the injection composition, the tubes are removed from the structure or cut flush with the surface of the structure, and the boreholes are sealed with polymer cement mortar.
Depending on the design, the nature of the destruction, the strength of the material and the depth of the pipe burial, the appropriate pressure is assigned for each individual case. As the well is saturated, the pressure gradually increases to the maximum set for a given structure and material.
The applied pressure should not compromise the strength of the structure and cause any deformation. During the injection process, a moment comes when the well stops accepting the solution, and a rapid rise in pressure indicates that the existing voids in the structure are filled and further injection should be stopped.
Sometimes injection is carried out in several stages with a break of one day. Re-injection is especially useful in underground structures, where there may be voids behind the wall, and the solution exiting through the through cracks creates layers and fills the voids between the structure and the ground.
The amount of injected cement mixture in one well depends on the volume of the structure, its location, the nature and size of the defect, and the correct placement of the pipes.
A lot of the mixture leaves when injecting underground structures due to the lack of proper compaction of the soil, the presence of various foreign inclusions in it - construction waste, formwork boards, frozen clods of soil, etc. In this case, the solution sometimes spreads over considerable distances from the place of cementation ().
At the end of the work, the injection plastic tubes are removed either by cutting them flush with the structure, or by removing them from the concrete body, if no more than 16-24 hours have passed after the end of the injection. The remaining holes are filled with mortar.
3.5.3. The technology of reinforcing underground and aboveground parts of buildings with polymer compositions by the injection method is performed in the following sequence:
Boreholes are drilled Æ 20 - 25 mm along the axis of cracks in defective zones or over the entire area of \u200b\u200bthe structure. The injection technology, pitch, diameter, depth of holes depend on the nature of the damage and are determined by the author of the project at the site of work;
When compacting the material of structures (brick, stone, concrete, reinforced concrete) with undetected defects, the spacing of the holes is taken at the rate of 10 - 20 pcs / m2 of surface, and the depth of the holes is 2/3 of the thickness of the structure (;);
When creating horizontal waterproofing in external and interior walls the spacing of the holes is taken no more than 150 mm, the holes are arranged in two, three or more rows in a checkerboard pattern with a height offset of 100 - 150 mm (.;.;.);
Drill cuttings are removed from the holes in any way;
Metal tubes are installed in the holes of the holes (fittings 10-15 cm long, which are reinforced with cement or polymer-cement mortars. In case of dense concrete (stone), the installation of tubes is optional, in this case the injection is carried out using injectors;
For sealing cracks and in some cases (usually when brickwork) the surface of structures in order to prevent leakage of injection compositions from it, as well as leveling the surface of brick or stone structures (in the case of a subsequent installation of paint waterproofing), polymer-cement plaster with a thickness of 10 - 20 mm (.) is performed.
Equipment for injection work is being prepared.
Injectable compositions are being prepared.

Fig. 3.7. Injection and cover waterproofing device
3.5.4. Technological operations and equipment for drilling holes:
The special technology of NIIMosstroy includes the following technological operations:
marking of drilling sites.
drilling holes,
installation of plastic pipes in the holes,
monolithing of pipes with cement mortar - BUS,
injection or pouring into the hole of special compounds that fill microcracks and pores in the body of the wall and foundations and protect against water penetration;
The most time-consuming and demanding operation is drilling blind inclined holes of a cylindrical shape with a diameter of 18 - 25 mm and a depth of up to 1 m. The angle of inclination of the holes and the horizontal plane is ~ 25 °, the distance from the floor is ~ 100 mm. The holes are staggered, the distance between them horizontally and vertically up to 150 mm;
The most effective means of making holes is the mechanization of these works using various types of hand-held perforators. Right choice determines the optimal labor intensity and quality of the holes;
The mechanical method makes it possible to obtain holes by drilling, drilling, punching, cutting the material of the building structure, or a combination of these methods, for example, rotary percussion drilling;
Of all the mechanical methods of drilling holes, the most effective is the shock-rotary one, since the wear of the RI during such drilling is approximately equal to the average amount of wear with other methods (shock-rotary, rotary);
For making holes with a diameter of 18 - 25 mm, a depth of up to 0.1 m, the most suitable are manual electric drilling machines of heavy type with a drilling diameter of up to 23 mm, such as RN-38 by AEG, GBN 7/45 by BOSCH, VN45E by ELU, equipped with carbide-reinforced twist drills;
The drills have universal slotted shanks, which allows the use of drills from various foreign companies.

Fig. 3.8. Wall strengthening scheme
3.5.5. Technological operations, equipment and tools for injection and creation of a waterproofing barrier:
drilling and hole cleaning,
primary filling of holes with a polymer-cement composition,
re-drilling and cleaning of holes,
injections from working formulations GU-412e and GUI-412e,
re-filling the holes with polymer-cement mortar;
The initial filling of the holes with a polymer-cement composition is performed after they have been cleaned from drill cuttings. Filling and cleaning the holes from drill cuttings can be done in any available way (flushing, blowing, mechanical removal etc.);
The holes are filled through pipes without overpressure by a lever-type hand pump specially made for injection cement mortars, previously passed through a sieve of 0.63 mm. After filling, before carrying out further work, a technological pause of at least one day is maintained;
re-drilling of the hardened material and cleaning of the holes is carried out after at least one day to the entire depth of the hole with the same diameter drill as in the initial drilling. Cleaning is carried out by flushing, blowing, mechanical removal, etc .;
The injection of the working composition is carried out after cleaning the holes from drill cuttings under a pressure of 0.1 - 0.2 MPa with the same pump or repeated pouring without pressure until full saturation;
The injection time under pressure is usually 5 - 10 minutes, the pressing is considered complete when on the outer surface around the hole into which the injection is made, the working composition protruding on the surface becomes noticeable in the form of a round wet spot. If this is impossible to determine, then a special graduated glass tube is glued to the surface and filled with special compounds, and the saturation of the wall is determined by the consumption of this composition;
Re-filling of the holes with polymer-cement material is performed after injections with the working composition with a technological pause until complete saturation.
3.5.6. Safety precautions in the production of injection works.
When performing work on injection strengthening and waterproofing of structures of buildings and structures with compositions based on modified compositions, it is necessary to observe the rules provided for in the chapter of SNiP III-4-80 * "Safety in construction"; SN 245-71 "Sanitary standards for the design of buildings and structures."
It is necessary to systematically monitor the state of the air environment in the premises and the concentration harmful substances in working area, avoiding exceeding the maximum permissible concentrations (according to the sanitary standards for the design of enterprises). Indoor work can be carried out if there is effective ventilation in the basement.
Before being admitted to independent work, workers must be instructed in safety and fire safety.
Those working with polymer materials and compositions must have overalls and personal protective equipment (cotton gowns, cotton suits and rubber gloves).
In case of contact of the formulations on the skin, it is necessary to clean the skin area with a swab and rinse with plenty of warm water.
The premises must be provided fire safety: Provide fire prevention system and fire protection system.
Persons at least 18 years of age who have undergone special training and received a certificate for the right to work with these tools, as well as certified in the first group of safety precautions, are allowed to work with pneumatic tools.
In the event of malfunctions in the operation of the mechanisms, the necessary repairs are allowed only after they have been stopped, the power is disconnected and the supply of compressed air is cut off.
All electrical housings must be reliably grounded.
4. TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR POLYMER AND POLYMER CEMENT FIXING AND WATERPROOFING COMPOUNDS
4.1. Application area.
The compositions are used for waterproofing concrete, masonry, plaster in underground structures (inside and outside), sewage treatment plants, water tanks, swimming pools, heating plants, mines, dams, sluices.
4.2. Requirements for covering materials.
Covering materials should:
have a waterproofing property;
be resistant to the action of water-soluble salts;
be resistant to aggressive substances;
have an antiseptic effect;
have good adhesion to masonry or concrete.
4.3. Materials used for covering waterproofing.
For the installation of coating coating waterproofing materials are used based on organosilicon compounds - GU-412e and on the basis of cement-containing coatings - Aquafin-1K, Aquafin-2K and others.
4.3.1. Polymer composition GU-412e:
It is a composition consisting of a mixture of silicic acid esters with a solvent without dilution and a hydrophobic composition based on GKZH-Pe without dilution - two-component for covering waterproofing.
Designed for preservation of building materials, structural strengthening and for cover hydrophobization of inorganic porous materials, used for external and internal work;
Produced in accordance with the technological regulations approved in accordance with the established procedure;
In terms of physical and chemical indicators, it must comply with the requirements and standards specified in table.
The composition is prepared at the workplace in accordance with TU 2312-009-04000633-96.
Toxic and flammable before application to the surface.
Storage: in tightly closed glass containers in accordance with GOST 9980-1-86 *; shelf life 1 year.
The polymer composition is transported at a temperature not higher than + 30 ° C.
Consumption: for covering treatment for 1 m 2 - 0.5 l.
4.3.2. Waterproofing coating Aquafin-1K by Schomburg:
Supplied in powder form and prepared in a clean container with added the required amount clean water;
By stirring, it is brought to a consistency suitable for use with brushes, brushes or sprayers and applied to the prepared surface;
Does not contain substances that have a destructive effect on reinforcement and concrete.
After hardening, forms a durable hard coating.
If cracks may appear on the surface, then such surfaces should be treated with Aquafin-2K insulating agents.
4.3.3. Elastic cover waterproofing Aquafin-2K:
An elastic waterproofing coating consisting of three parts by weight of Aquafin-1K and one part by weight of Uniflex-B (liquid elasticizer);
The hardened coating Aquafin-2K resists the negative pressure of groundwater and stagnant water and is elastic enough to bridge hairline cracks;
It is also used for waterproofing surfaces to be coated ceramic tiles (pools, water storage tanks, etc.) and for terraces, balconies, roofs and during the restoration of old buildings;
In cold rainy weather and with highly damp surfaces, you should first put a primer tie coat Aquafin-F and immediately Aquafin-1K.
Examples of waterproofing basements, underground garages, balconies, under tiles, etc. are given on; ; ;
– new technology, widely used for strengthening and insulating foundations of new buildings and existing construction projects. Effective method, which allows you to create a reliable waterproof membrane between structures and an aggressive environment.
In this article, we will consider the waterproofing of objects by injection, the features of the technology, how the work is done, what is required for them, as well as its advantages and disadvantages.
What is injection waterproofing?
Is a waterproofing based on liquid polymers, pumped under pressure and works directly inside the building structure or in specially organized sections designed to minimize the consumption of the injection composition and the possibility of localizing a leak.
After getting into the structure, helium polymer compositions polymerize, as a rule, within an hour, after which they acquire the ability to withstand very high pressure Wednesday.
Application area
The method has long been used in foreign countries. In Russia, this unique technology has appeared recently, but has already gained popularity in the construction and repair industry.
This technique involves the injection of waterproofing compounds into the material of the foundation and other building elements that are subject to destruction under the influence of a humid environment. For insulation work, special materials and equipment will be required.
The main goal is to strengthen and protect the foundation from destruction provoked by a humid environment. This method is relevant for increasing the bearing capacity of the foundation, for consolidating the soil and sealing the formed cracks.
Modern technology is also used to eliminate the inflow of water formed in the foundation, and to arrange shut-off waterproofing between the foundation and the wall of the building.
Technology
It is carried out using a special technology. All materials used remain liquid for 30-40 minutes. Their hardening is controlled by the catalysts included in the composition. Experts recommend carrying out work at a temperature of at least 5 degrees.
Waterproofing injection methods
The selection of the procedure depends on the selected material and the surface to be insulated.
Where the technology is applied:
- For injecting the foundation. The best option - the use of a cement-sand composition based on silicates.
- For waterproofing walls during the construction phase and during overhaul... It is recommended to use acrylic or polyurethane material.
- For injection of basements and basements.
- In order to strengthen the base of concrete structures, joints and cracks are waterproofed.
- To improve the quality of a brick building, waterproofing is performed by injection using hydrophobic compounds.
- For reinforcing old foundations and restoring bearing capacity.
- For insulating cold joints in reinforced concrete structures, etc.
Ways of applying injection waterproofing:
- "By gravity" - involves filling holes drilled at an angle with material and its subsequent movement under the influence of gravity. When performing insulation with this method, fast-hardening compounds cannot be used.
- "Under pressure" - filling of materials takes place under a pressure rush. The pressure is supplied by a pressure pump. It is possible to carry out work on this technology only in warm weather (at least 5 degrees Celsius).
Equipment for injection waterproofing
For waterproofing works injection method you will need a special metal packer and a high pressure pump.
Materials (edit)
The foundations and other building surfaces are made using different materials.
What materials can be used:
- Polyurethane polymer is a highly plastic material that withstands various loads well. Economical consumption. Affordable cost. It is widely used for insulation of foundations located on the territory of quicksand and loose soil.
- Acrylic gel is a durable and resistant material. Easily penetrates the smallest pores of the foundation. It hardens quickly. Particles of soil are used to strengthen the material, which provides additional protection against washout.
- Epoxy material - used in dry construction. Cures quickly on contact with air. After complete polymerization, the solid membrane is completely impermeable to water.
- Siloxane or silicate based materials. When interacting with the basic building material, they are converted into an emulsion, which creates a highly effective barrier to water. Can be used for waterproofing surfaces with high humidity.
Stages of work
Waterproofing works by the injection method are carried out in stages, in accordance with important technological rules.
Stages of carrying out:
- Examination of the surface with the identification of points of localization of moisture penetration.
- Drilling through holes with a step of up to 0.5 m. Diameter - up to 20 mm. Additional holes are made in places of localization.
- Drilling blind holes along the fault line or cracks.
- Metal packers are inserted into the holes created, ball valves are fixed to their outer part.
- A tank with a waterproofing compound is connected to the ends of the fixed taps.
- The composition is transported through the tube by gravity or under the influence of pressure (depending on the selected injection method).
- After the material has hardened, the tubes are removed.
- The outer surface is covered with a layer of moisture-resistant plaster or cement-sand mortar.
Advantages and disadvantages
It has many advantages. This technique eliminates the need for land work when strengthening the foundation of already finished buildings. The mixtures used do not contain harmful impurities, therefore they are absolutely safe for the human body.
Due to the low density of the compositions, a high penetrating power of the material is ensured. When carrying out work, it is not necessary to pre-dry, injection gels have good adhesion to wet surfaces. It is possible to carry out waterproofing even in cold weather, the main thing is to choose the appropriate material adapted to low temperatures.
What other advantages does injection waterproofing have:
- you can perform work during the construction phase and after the construction of the building;
- the technology is used for overhaul;
- the result is a guaranteed high-quality waterproofing with a reliable membrane that envelops the entire surface.
The disadvantages include the high cost of materials, the need to use special equipment and the mandatory observance of technological rules. In the absence of skills, it is better to entrust this work to specialists.
Features of injection of various designs
It is carried out according to the standard scheme, but has some peculiarities when performing work on different construction sites.
To improve the operational characteristics of the erected building, injection of walls is performed. Work is carried out even at the construction stage or during a major overhaul.
When injecting the foundation, vertical waterproofing is performed with the creation of a horizontal barrier that prevents moisture penetration.
External and internal waterproofing is carried out when injecting basements.
To strengthen the foundations of concrete structures, waterproofing of cold and moving joints is performed.
To increase the strength and moisture resistance of brick structures, insulation is made using hydrophobic compounds.
Today, specially trained craftsmen who have all the necessary equipment in their arsenal are of high quality.
Today, the term "injection waterproofing" can be understood as a very wide area of \u200b\u200bwaterproofing work.
Moreover, there is often a substitution of concepts or the usual confusion.
The purpose of this article is not the ultimate truth, but our idea of \u200b\u200bthis, currently quite popular, concept that we want to convey to you, based on a specific example: the availability of materials for injection waterproofing in the line of materials of the PENETRON waterproofing system.
To begin with, let's understand a little in terms so that we ourselves do not allow the substitution of concepts or confusion.
Waterproofing is a sequence of measures using special building materials, the purpose of which is to prevent contact with a specific building structure or to prevent water from entering the building structure.
Types of waterproofing
All of the above types of waterproofing have the following disadvantages:
- they all form a waterproof coating on the concrete surface
- with the exception of plaster waterproofing, they all require a protective coating against mechanical damage
- in case of mechanical damage or destruction of the integrity of the waterproofing coating created with their help, the concrete structure becomes defenseless against the effects of water
- to prevent contact or penetration of water into a concrete structure, all the above types of waterproofing can only be used during the construction phase, since they are applied only from the outside of the protected structure, forming a waterproofing coating on the concrete structure from the ground (for underground structures) or water (for structures that come into contact with water during operation)
- when water penetrates into the room, to restore the waterproofing of the above types, a complete excavation of the structure is required, the creation of a new waterproofing coating and backfilling of the pit.
Penetrating and injection waterproofing: buy and waterproof concrete
The following types of waterproofing are fundamentally different from those listed above, since they change the internal structure of the concrete structure in different ways, transforming the concrete itself into a waterproof environment.
These types of waterproofing can be divided into the following categories:
1. Penetrating (penetrating) waterproofing:
The principle of operation of this waterproofing is due to the special chemical composition a waterproofing material of penetrating action and a method of "delivery" of these special chemical components inside the concrete mass, followed by a change in the structural composition, giving the structure the property of watertightness.
The second name of this type of waterproofing is penetrating, it is no coincidence.
So this type of waterproofing began to be called by the name of the company, which 50 years ago was the first to produce waterproofing materials of penetrating action - PENETRON.
And when these materials began to gain more and more popularity every year, then these materials, and then the type of waterproofing, began to be called "penetrating".

2. Injection, or injection waterproofing, the price of which, by the way, is quite low:
To perform waterproofing works using the technology of injection waterproofing, special equipment is required, since, unlike penetrating waterproofing (when waterproofing material penetrating action "PENETRON" penetrates into the concrete as a result of physical processes, and water resistance is imparted to the concrete throughout the entire thickness of the concrete as a result chemical processes)
injection materials are pumped into the concrete under pressure with special pumps.
In addition, injection materials, in contrast to the penetrating material, are not chemically similar to concrete, usually these are polymer compositions, which, due to their initial viscous-flow state, are called injection resins.

Since injection resins have a much higher viscosity than water, they cannot fill the capillaries of concrete, therefore, concrete injection, as a rule, is the work of waterproofing cracks formed during operation.
Injection resin, for example, when it penetrates into cracks in the floor or walls, turns into a solid state, reliably waterproofing static cracks, that is, not subject to deformation.
But, often, cracks in concrete are formed in those places where periodic deformations of concrete occur.
Cracks in such places are characterized by a change in the width of their opening over time.
They are called dynamic, and for their waterproofing, injection resin is used, which, after hitting the floor or walls, forms an elastic filling of the crack cavity, which makes it possible to provide waterproofing when the crack opening width changes.
If water flows out of the crack, the cavity of which must be filled with injection material, then before applying injection waterproofing it is necessary to stop this leak.
For this, the concrete is injected in such a way as to get into the crack as close as possible to the outside of the concrete structure.
In this case, an injection resin is used which is hydroactive, i.e. which, upon contact with water, begins to increase in volume very quickly, filling the crack, thereby preventing the flow of water. After the water stops flowing, the cavity is filled with injection resin, which creates a durable waterproofing of the cavity.

Injection resins, included in the PENETRON waterproofing system line of materials, are effective materials for creating waterproofing cracks that have arisen during the operation of concrete structures by injection (injection) into concrete. You can buy injection waterproofing in the Penetron-Moscow company.
| Materials for creating injection waterproofing | |||||
| Material name | Description | Features of the | Cost, rub. (in view of VAT) | ||
| PENESPLITSIL | Two-component polyurethane resin for injection into dry and wet cracks, including mobile ones. The polymerization time is 40 minutes. Purpose: sealing static and mobile cracks, cutting off the capillary rise of moisture. | Low viscosity, which makes it possible to seal cracks with an opening width of 0.15 mm; High adhesion to concrete, metal and plastic; Resin reaction products are resistant to acids, alkalis and microorganisms. | Metal cans 19.2 kg + 22.8 kg | 46 872,00 | |
| PENEPURFOM | A two-component, hydroactive polyurethane resin that foams on contact with water to form a waterproof foam. Purpose: stopping pressure leaks through cracks. There are three types of material with different cure times: 1. PenePurFom N - 5 min. 2. PenePurFom HP - 3 min. | Low viscosity, due to which the material penetrates into cracks with an opening width of 0.15 mm; The ability to seal cracks and seams through which water is abundantly filtered; The ability to select the required type of material, depending on the intensity of water filtration. | Metal cans 20 kg + 24 kg | 36 212,00 | |
| 3. PenePurFom R - 1.5 min. | 36 617,00 | ||||
| PENEPURFOM 65 | One-component, hydroactive, injection material based on polyurethane resins. Foams on contact with water to form a waterproof rigid foam. Purpose: stopping pressure leaks through static cracks in concrete, brick and stone structures. | The ability to control the polymerization time using a catalyst; The ability to seal cracks and seams through which water is abundantly filtered; The ability to effectively fill voids and compact the soil behind the structure, thanks to the low viscosity and large increase in resin volume (65 times). | Metal canister | 19 680,00 | |
| Material name | Description | Features of the | Cost, rub. (in view of VAT) |
|
| PENEPURFOM 1K | One-component, hydroactive, injection material based on polyurethane resins. Foams on contact with water to form a waterproof resilient foam. Purpose: stopping pressure leaks through static and moving cracks; filling the cavity of expansion joints. | The ability to control the polymerization time using a catalyst; The ability to seal cracks and seams through which water is abundantly filtered; The ability to effectively seal moving cracks due to the elasticity of the material. | Metal canister | 17 820,00 |
| Catalysts for one-component resins |
||||
| Catalyst PenPurFom 65 Catalyst - an accelerator that significantly reduces the polymerization time of the polyurethane resin "PenePurFom 65" | Metal can 1 kg | 2 070,00 |
||
| Catalyst PenePurFom 1K The catalyst is an accelerator that significantly reduces the polymerization time of the polyurethane resin "PenePurFom 1K". | Metal can 1 kg | 2 340,00 |
||
| Equipment |
||||
| Manual piston pump EK-100M Designed for injecting polyurethane resins. | 32 000,00 |
|||
| Piston pump with electric drive EK-200 Designed for injecting polyurethane one- or two-component resins. | 90 000,00 |
|||
| Injector (packer) for piston pumps EK-100 and EK-200. | ||||
Buildings made of concrete and bricks are strong, stable, capable of withstanding strong mechanical loads and temperature drops. But joints remain between the slabs, groundwater penetrates into the expansion joints, and any crack in the wall can become a source of leakage. Waterproofing concrete foundation, masonry or masonry helps prevent the "deluge". With its help, it is possible to eliminate the existing leaks and, by sealing the cracks in the slabs, prevent the appearance of new ones.
Waterproofing by injection means restoring the integrity of the system with a hydrophobic material. During the work, a polymer is injected: a substance is pumped under pressure into the destroyed structure. Varmastroy uses powerful pumps that are safe for concrete slabs and bricks. The advantage of the method is that there is no need to dismantle structures for the sake of injection.
"Varmastroy" conducts injection recovery:
- working (cold) seams;
- expansion joints;
- microdefects and cracks;
- inputs engineering communications;
- junction nodes.
The contractor proposes a shut-off isolation device. All work is carried out using modern European sealants.
Cold seams
It is technologically impossible to fill all concrete structures at the same time. A molecular tension arises between the old, already frozen, and new layer. Sooner or later, water begins to ooze through the working seam. The liquid destroys the concrete slab and the reinforcement inside. As a result, the strength of the entire structure is reduced.
Defects locations:
- flat or ribbed floors;
- foundation;
- columns;
- beams.
Insulation installation procedure:
- Workers are chasing a cold seam.
- They clean it from dust and mint it with a repair mixture.
- Holes are drilled for the injection mixture.
- Install packers.
- The defect is sealed with polyurethane foam, then with polyurethane resin.
- Packers are removed.
- Grind problem area diamond tool.
- Cover the surface of the seal with a sealant.
Expansion joints
Construction technology sections divide the building into “stand-alone” blocks. This separation allows you to level the load on bearing structures, to prevent critical deformation of the building.
In the hollow space, water flowing down can accumulate, and ground streams can penetrate through the cracks. Over time, the depression cracks and ceases to hold the liquid.
Insulation installation procedure:
- Workers remove the old grout.
- Layer-by-layer new sealant.
- The cavity is raked with a repair mixture.
- Holes are drilled at an angle to the longitudinal line.
- Install packers.
- Acrylate gel is pumped under pressure.
- Packers are removed.
- Seal the holes with a hydrophobic compound.
- An epoxy-based tape is glued on top.
Cracks
Micro-fractures in cement or brick quickly develop into crevices, voids, or gaps. High humidity only speeds up the process. Cracks are formed due to improper design of the building, excessive loads, seismic shifts, redistribution of the weight of the upper floors.
The reasons for non-structural defects are general shrinkage of the structure, strong temperature drops, destruction of internal reinforcement. Such slots do not affect the mechanical strength, but they serve as sources of water flows.
Insulation installation procedure:
- 1. Workers are ditching the crack.
- 2. Clean the insulated surface, stamp it with a repair mixture.
- 3. Drill holes at an angle to the baseline.
- 4. Install packers.
- 5. By pressure, polyurethane foam is fed into the fracture.
- 6. After solidification, the polyurethane resin is injected.
- 7. Remove packers.
- 8. Grinding the areas adjacent to the defect with diamond equipment.
- 9. Coat the surface with a sealing compound.
Communication inputs
Water, electrical cables, natural gas are supplied to the building through pipes. Holes are made in the walls of the building into which steel sleeves are inserted. Waste water and groundwater seep through leaking gaps. They stagnate indoors, provoking further destruction of concrete. Prices are per m2.
Insulation installation procedure:
- 1. Workers are embroidering the interface.
- 2. Seal the space between the wall and the pipe with polymer sealant.
- 3. The joint is stamped with a repair mixture.
- 4. Drill holes around the bushing.
- 5. Install packers.
- 6. An insulating compound, an acrylate gel, is introduced under pressure.
- 7. Remove packers.
- 8. Seal the holes with repair compound.
- 9. Coat the place of work with a hydrophobic substance.
Adjacency nodes
Water also penetrates through the joints between:
- - walls and horizontal slabs;
- - columns and floor or ceiling;
- - openings or arches and ceilings.
Water accumulates in the cracks, which further accelerates the destruction. To prevent collapse, microdefects must be sealed. The price of work is calculated per m.
Insulation installation procedure:
- 1. The workers sew the joint.
- 2. Coal it with a building mixture.
- 3. Arrange a fillet.
- 4. Drill holes on either side of the main line.
- 5. Install packers.
- 6. Seal the assembly first with polyurethane foam, then with polyurethane resin.
- 7. Remove packers.
- 8. Close up the holes.
- 9. Grind the surface and coat it with sealant.
Shut-off waterproofing
In the foundation, moisture accumulates under the influence of groundwater. It penetrates inside, leads to the rapid destruction of concrete, the spread of fungus, microorganisms.
Insulation installation procedure:
- Workers drill holes around the perimeter, at a distance of 100–120 millimeters. The angle is selected depending on the foundation.
- Clean the surface from dust.
- Packers are mounted.
- An injection composition is supplied under pressure.
- Packers are removed.
- The holes are closed with a hydrophobic substance.
The following types of polymer injection compounds are used in construction for injection of concrete, cracks, masonry, as well as waterproofing shutoff:
Polyurethane resins (PUR):
- for elastic sealing and filling of dry, wet and water-saturated cracks, seams and joints in above-ground, underground and engineering structures, including drinking water facilities
- to create a shut-off waterproofing against the rise of capillary moisture on brick and stone walls.
- for injecting concrete into injection hoses laid before it is laid in a structure, intended for sealing working joints in reinforced concrete structures.
- hydroactive polyurethane resins (foams) are used when there is a lot of water entering the structure, to eliminate filtration and infiltration of water under significant pressure.
Acrylate based resins (gels) (A):
- for additional external sealing of building structures buried in the ground (waterproofing cut-off) by injecting gel along the border of the soil-building structure.
- for sealing and sealing injection of cracks and voids in masonry and concrete
- for elastic sealing and filling of wet microcracks in concrete and stone structures
- to create a waterproofing cutoff from the rise of capillary moisture along brick and stone walls
- for soil consolidation
- Work experience 25 years - since 1993!
- More than 900 completed projects!
- Prompt departure for the assessment of the object: 1-2 working days.
- Departure in Moscow and the nearest Moscow region - FREE OF CHARGE!
- Execution of works in accordance with GOST, SNiP.
- SRO admission.
- Only high quality material is used.
- The warranty for the work performed is up to 12 years!
- Cleanliness and order at the facilities during the work!
In this article:
The need for waterproofing
Modern building codes oblige developers to carry out work related to the external waterproofing of parts of buildings and structures located underground. Thus, for example, before closing the pit from the outer part of the basements of buildings, underground passages, waterproofing should be applied. This insulation method creates the effect of "pressing" the protective layer to the outer part of the structure, which additionally prevents water penetration. Installing insulation inside buildings leads to the opposite, "squeezing" effect, which over time affects the insulating properties.
Today the highest quality and reliable protection against water penetration can be achieved by applying the method injection waterproofing... This method appeared quite recently, but, nevertheless, most experts believe it with confidence. the best method isolation of underground structures of buildings and structures from the effects of water.
Advantages of injection waterproofing
Compared to other methods injection waterproofing has a number of advantages:
- Significant savings in repair and construction works:
- a) insulation can be repaired in local areas.
- b) the amount of work is minimal both in time and in terms of money.
- c) there is no need to stop the operation of the facility.
- d) there is no need for earthworks in the case of underground waterproofing.
- The method is applicable at any time of the year.
- Waterproofing is monolithic - it has no seams or joints.
Injection waterproofing - all-season,
performed from inside the premises
Features of injection technology




This method involves drilling through holes in the surfaces of structures. Through these holes, using elongated packers under high pressure, the injection solution is pumped into the outer part of the structures. The compositions of insulating solutions are different, their choice is due to the water-absorbing properties of the surrounding soils. To fill large voids, fine-grained compositions based on cement binders, acrylic gel, low-viscosity polyurethane resin are used. Each composition requires compliance with special rules when working with it, compliance temperature regime, the use of special pumps for injection, etc. Solutions for injection have different response capacities: slow, fast, instant.
According to many experts, the most effective and practical in terms of quality and price are polyurethane compositions PeneSplitSeal and PenePurFoam. They are resistant to physical stress, plastic. In the process of interaction with water, they polymerize. They are hydroactive. Polyurethane compounds are used for waterproofing wet and dry cracks, as well as for permanent sealing of moving holes.
In addition, by the injection method, it is possible to completely protect the outer part of the building wall when working from the inside. Sometimes this method of waterproofing is called "veiled". The veil waterproofing is carried out by means of polyurethane material using a one-component pump. After preparatory work and the marking of drilling holes is made directly by creating through holes at an angle of 90 degrees.
Applications
Injection waterproofing is applicable:
- on concrete
- brick by brick
Examples of objects on which the most expedient use of injection waterproofing are:
- Tunnels, stations, subway structures;
- Foundations of buildings;
- Basement floors;
- Underground garages;
- Cellars;
- Bridge supports;
- Underground concrete tanks



