Do-it-yourself welding machine: simple instructions for creating and using the device. How to make a welding machine with your own hands How to make a welding machine yourself
In our time, it is difficult to imagine any work with metal without using a welding machine. With this device you can easily connect or cut iron different thicknesses and dimensions. Naturally, to perform quality work, you will need certain skills in this matter, but first of all you need the welder himself. Nowadays, you can naturally buy it, as, in principle, and hire a welder, but in this article we will talk about how to make a welding machine with your own hands. Moreover, with all the wealth of various models, reliable ones are quite expensive, and cheap ones do not shine with quality and durability. But even if you decide to buy a welder in a store, familiarity with this article will help you choose the required device, since you will know the basics of their circuitry. There are several types of welders: DC, AC, three-phase and inverter. In order to determine which option you need, consider the design and device of the first two types, which can be assembled with your own hands at home without specific skills.
AC
This type of welding machine is one of the most common options, both in industry and in private households. It is easy to operate, compared to the rest, it can be made quite easily at home, which is confirmed by the photo below. To do this, you need to have a wire for the primary and secondary windings, as well as a transformer steel core for winding the welder. In simple words AC welder is a high power step-down transformer.
The optimum voltage for a home-assembled welding machine is 60V. The optimal current is 120-160A. Now it is easy to calculate what cross-section the wire should have in order to make the primary winding of the transformer (the one that will be connected to the 220 V network). Minimum cross-sectional area copper wire should be 3-4 sq. mm, the optimal one is 7 sq. mm, because it is necessary to take into account the possible additional load, as well as the necessary margin of safety. We get that optimal diameter the copper core for the primary winding of the step-down transformer should be 3 mm. If you decide to take an aluminum wire in order to make a welding machine with your own hands, then the cross-section for a copper wire must be multiplied by a factor of 1.6.
It is important that the wires are in a rag sheath; PVC-insulated conductors cannot be used - it will melt and occur when the wires are heated. If you do not have a wire of the required diameter, then you can use thinner cores, winding them in parallel. But then it should be borne in mind that the thickness of the winding will increase, and, accordingly, the dimensions of the device itself. It should be borne in mind that the limiting factor may be a free window in the core and the wire may simply not fit there. For the secondary winding, you can use a thick stranded copper wire - the same as the core on the holder. Its cross-section should be selected based on the current in the secondary winding (recall that we are focusing on 120 - 160A) and the length of the wires.
The first step is to make the transformer core of a homemade welding machine. The best option would be a rod-type core as shown in Figure 1:

This core must be made from transformer steel plates. The thickness of the plates should be between 0.35 mm and 0.55 mm. This is necessary to reduce. Before assembling the core, you need to calculate its dimensions, this is done as follows:
- First, the window size is calculated. Those. dimensions c and d in Figure 1 must be selected to accommodate all transformer windings.
- Secondly, the roll area, which is calculated by the formula: Scroll \u003d a * b, must be at least 35 sq. see. If the S roll is greater, then the transformer will heat up less and, accordingly, work longer, and you will not have to interrupt frequently in order for it to cool down. It is better that the Skren be equal to 50 sq. cm.
Next, we start assembling the plates of a homemade welding machine. It is necessary to take the L-shaped plates and fold them, as shown in Figure 2, until you can make the core of the required thickness. Then we fasten it with bolts in the corners. At the end, it is necessary to process the surface of the plates with a file and insulate them by wrapping them with rag insulation in order to additionally protect the transformer from breakdown onto the case. 
Next, we proceed to winding the welding machine from a step-down transformer. First, we wind the primary winding, which will consist of 215 turns, as shown in Figure 3. 
It is advisable to branch off from turns 165 and 190. We attach a thick textolite plate on top of the transformer. We fix the ends of the windings on it using a bolted connection, noting that the first bolt is a common wire, the second is a branch from 165 turns, the third is a branch from 190 turns and the 4th is from 215. This will make it possible to subsequently adjust the amperage during welding by switching between different terminals of your welding device. This is a very important feature, and the more taps you make, the more precise your adjustment will be.
Then we start winding 70 turns of the secondary winding, as shown in Figure 4. 
Fewer turns are wound on the other side of the core - where the primary winding is wound. The ratio of turns should be made about 60% to 40%. This contributes to the fact that after you catch the arc and start welding, eddy currents will partially cut off the work of the winding with a large number of turns, which will lead to a decrease in the welding current, and accordingly improve the quality of the seam. Thus, the arc will be easy to catch, but too much current will not interfere with high-quality cooking. We also fix the ends of the winding with bolts on the textolite plate. You can not attach them, but lead the wires directly to the electrode holder and the crocodile to ground, this will remove the connections, where there can be potential for voltage drop and heating. For better cooling, it is highly desirable to install a fan for blowing, for example from a refrigerator or microwave.
Now your homemade welding machine is ready. Having connected the holder and ground to the secondary winding, it is necessary to connect the network to the common wire and the wire extending from the 215th turn of the primary winding. If you need to increase the amperage, then you can make fewer turns of the primary winding by switching the second wire to a contact with fewer turns. The current can be reduced by using a resistance made of a piece of transformer steel bent in the form of a spring, connected to the holder. It is always necessary to ensure that the welding machine does not overheat, for this, regularly check the temperature of the core and windings. For these purposes, you can even install an electronic thermometer.
This is how you can make a welding machine from a step-down transformer with your own hands. As you can see, the instructions are not too complicated and even an inexperienced electrician can assemble the device on his own.
Direct current
Some types of welding require a DC welder. This tool can be used to cook cast iron and stainless steel. You can make a do-it-yourself DC welding machine in no more than 15 minutes by redoing a homemade AC machine. To do this, a rectifier assembled on diodes must be connected to the secondary winding. As for the diodes, they must be able to withstand 200 A and have good cooling. For this, diodes D161 are suitable.
Capacitors C1 and C2 with the following characteristics will help us to align the current: capacity 15000 uF and voltage 50V. Next, we collect the circuit, which is indicated in the drawing below. Choke L1 is required for current regulation. Contacts x4 are plus for connecting the holder, and x5 is minus for supplying current to the part to be welded.

Three-phase welding machines are used for welding in industrial conditions, they have two-electrode holders, so we will not consider them in this article, and inverters are made on the basis of printed circuit boards and complex circuits with a large number of expensive radio components and a complex setup process using special equipment. However, we still recommend that you familiarize yourself with the inverter design in the video below.
Visual master classes
So, if you decide to make a welding machine at home, we recommend watching the video tutorials provided below, which will clearly show how to assemble a simple welder yourself from scrap materials, and also explain to you some details and nuances of work:
Now you know the basic principles of the construction of welders and you can make a welding machine with your own hands, both on direct and alternating current, using the instructions from our article.
Also read:
The welding machine is a rather popular device both among professionals and among home craftsmen. But for domestic use, sometimes it makes no sense to buy an expensive unit, since it will be used in rare cases, for example, if you need to weld a pipe or put up a fence. Therefore, it will be wiser to make a welding machine with your own hands, investing in it a minimum amount of funds.
The main part of any electric arc welder is the transformer. This part can be removed from the old, unnecessary household appliances and make a homemade welding machine out of it. But in most cases, the transformer needs a little tweaking. There are several ways to make a welder, which can be both the simplest and more complex, requiring knowledge in electronics.
To make a mini welding machine, you need a pair of transformers removed from an unnecessary microwave oven... Microwave is easy to find from friends, acquaintances, neighbors, etc. The main thing is that it has a power in the range of 650-800 W, and the transformer is in good working order. If the stove has a more powerful transformer, then the apparatus will turn out with higher current rates.
So, the transformer removed from the microwave has 2 windings: primary (primary) and secondary (secondary).

Resale has more turns and a smaller wire section. Therefore, in order for the transformer to become suitable for welding, it must be removed and replaced with a conductor with a larger cross-sectional area. To remove this winding from the transformer, it must be cut off from both sides of the part using a metal hacksaw.

This must be done with special care so as not to accidentally hit the primary winding with the saw.

When the coil is cut off, its remains will need to be removed from the magnetic circuit. This task is much easier if the windings are drilled to relieve the metal stress.



Do the same with the other transformer. As a result, you will have 2 parts with a primary winding of 220 V.
Important! Remember to remove the current shunts (shown by arrows in the photo below). This will increase the power of the device by 30 percent.

For the manufacture of the secondary, you will need to purchase 11-12 meters of wire. It must be stranded and have cross section not less than 6 squares.

To make a welding machine, for each transformer, you will need to wind 18 turns (6 rows in height and 3 layers in thickness).


You can wind both transformers with one wire or separately. In the second case, the coils must connect in series.



The winding should be done very tightly so that the wires do not dangle. Further, the primary windings need connect in parallel.

The pieces can be screwed onto a small piece of wood to be tied together.

If you measure the voltage on the secondary of the transformer, then in this case it will be 31-32 V.

With such a homemade welder, metal with a thickness of 2 mm is easily welded with electrodes with a diameter of 2.5 mm.



It should be remembered that such a homemade apparatus should be cooked with breaks for rest, since its windings are very hot. On average, after each used electrode, the device should cool down for 20-30 minutes.
It will not be possible to cook thin metal with an apparatus made from a microwave, since it will cut it. To adjust the current, a ballast resistor or choke can be connected to the welder. The role of the resistor can be performed by a piece of steel wire of a certain length (selected experimentally), which is connected to the low-voltage winding.
AC welder
This is the most common type of metal welding machine. It is easy to make at home, and it is unpretentious to operate. But the main drawback of the device is large mass of step-down transformer, which is the basis of the unit.

For home use, it is enough that the device produces a voltage of 60 V and can provide a current of 120-160 A. Therefore for the primary, to which the 220 V household network is connected, a wire with a cross section of 3 mm 2 to 4 mm 2 is required. But the ideal option is a conductor with a cross section of 7 mm 2. With this cross-section, voltage drops and possible additional loads will not be terrible for the device. From this it follows that for the secondary, a conductor is needed that has 3 mm in diameter. If you take an aluminum conductor, then the calculated copper cross-section is multiplied by a factor of 1.6. For the secondary a copper bar with a cross section of at least 25 mm 2 is required
It is very important that the winding conductor is covered with rag insulation, since the traditional PVC sheath melts when heated, which can cause a turn-to-turn short circuit.
If you have not found a wire with the required section, then you can make yourself from several thinner conductors. But this will significantly increase the thickness of the wire and, accordingly, the dimensions of the unit.
First thing, the base of the transformer is made - the core... It is made from metal plates (transformer steel). These plates should have a thickness of 0.35-0.55 mm. The studs connecting the plates must be well insulated from them. Before assembling the core, its dimensions are calculated, that is, the dimensions of the “window” and the cross-sectional area of \u200b\u200bthe core, the so-called “core”. To calculate the area, use the formula: S cm 2 \u003d a x b (see figure below).

But it is known from practice that if you make a core with an area of \u200b\u200bless than 30 cm 2, then it will be difficult to obtain a high-quality seam with such an apparatus due to a lack of power reserve. And it will heat up very quickly. Therefore, the cross section of the core must be at least 50 cm 2. Despite the fact that the weight of the unit will increase, it will become more reliable.
For core assembly, it is better to use L-shaped plates and place them as shown in the following illustration until the part reaches the desired thickness.

At the end of the assembly, the plates must be fastened (at the corners) with bolts, then cleaned with a file and insulated with fabric insulation.
Now you can start transformer winding.

One nuance should be taken into account: the ratio of turns on the core should be 40% to 60%.This means that on the side where the primary is located, there should be fewer turns of the secondary. Due to this, when welding starts, the winding with more turns will be partially cut off due to the occurrence of eddy currents. This will increase the current strength, which will have a positive effect on the quality of the seam.
When the winding of the transformer is complete, the mains cable is connected to the common wire and to the 215 turn tap. The welding cables are connected to the secondary winding. After that, the contact welding machine is ready for work.
DC apparatus
To cook cast iron or stainless steel, a DC apparatus is required. It can be made from a conventional transformer unit, if to its secondary winding connect rectifier... Below is a diagram of a diode bridge welding machine.

Diagram of a welding machine with a diode bridge
The rectifier is assembled on D161 diodes, capable of withstanding 200A. They must be installed on radiators. Also, to equalize the ripple of the current, 2 capacitors (C1 and C2) of 50 V and 1500 μF are required. This wiring diagram also has a current regulator, the role of which is played by the choke L1. Welding cables are connected to contacts X5 and X4 (straight or reverse polarity), depending on the thickness of the metal to be connected.
Inverter from computer power supply
It is impossible to make a welding machine from a computer power supply. But it is quite possible to use its case and some parts, as well as the fan. So, if you make an inverter with your own hands, then it can easily be placed in the power supply case from a computer. All transistors (IRG4PC50U) and diodes (КД2997А) must be installed on radiators without using gaskets. For cooling parts, it is desirable use a powerful fansuch as Thermaltake A2016. Despite their small size (80 x 80 mm), the cooler is capable of developing 4800 rpm. The fan also has a built-in speed controller. The latter are controlled by a thermocouple, which must be fixed to a radiator with installed diodes.
Advice! It is recommended to drill several additional holes in the PSU case for better ventilation and heat dissipation. Overheating protection installed on the radiators of transistors is configured to operate at a temperature of 70-72 degrees.
Below is a schematic electrical diagram of a welding inverter (in high resolution), according to which you can make an apparatus that fits in the power supply case.
The following photos show what components a homemade inverter welding machine consists of, and how it looks after assembly.



Electric motor welder
To make a simple welding machine from an electric motor stator, it is necessary to select the motor itself that meets certain requirements, namely, that its power is from 7 to 15 kW.
Advice! It is best to use a 2A series motor as it will have a large magnetic circuit window.
You can get the required stator in places where scrap metal is accepted. As a rule, it will be cleared of wires and after a couple of blows with a sledgehammer, it splits. But if the case is made of aluminum, then in order to remove the magnetic circuit from it, need to anneal the stator.
Preparation for work
Place the stator with the hole facing up and place bricks under the part. Next, fold the wood inside and set it on fire. After a couple of hours of frying, the magnetic core will easily separate from the case. If there are wires in the housing, they can also be removed from the grooves after heat treatment. As a result, you will get a magnetic circuit, cleaned of unnecessary elements.

This blank follows well soak with oil varnish and let it dry. To speed up the process, you can use heat gun... The impregnation with varnish is done so that after removing the screeds, the package does not spill.
When the disc is completely dry using a grinder, remove the screedslaid out on it. If the ties are not removed, they will act as short-circuited turns and take the power of the transformer, as well as cause it to heat up.
After cleaning the magnetic circuit from unnecessary parts, you will need to make two end plates (see figure below).

The material for their manufacture can be either cardboard or press board. You also need to make two sleeves from these materials. One will be internal and the other will be external. Next, you need:
- install both end caps on the blank;
- then insert (put on) the cylinders;
- wrap all this structure with kiper or glass tape;
- soak the resulting part with varnish and dry.
Transformer manufacturing
After carrying out the above steps, a welding transformer can be made from the magnetic circuit. For these purposes, you will need a wire covered with fabric or glass enamel insulation. To wind the primary winding, you need a wire with a diameter of 2-2.5 mm. The secondary winding will require about 60 meters of copper bus bar (8 x 4 mm).
So, the calculations are done as follows.
- Twenty turns of a wire with a diameter of at least 1.5 mm should be wound onto the core, after which a voltage of 12 V must be applied to it.
- Measure the current flowing in this winding. The value should be about 2 A. If the value is greater than the required one, then the number of turns must be increased, if the value is less than 2A, then decrease.
- Count the number of turns obtained and divide by 12. As a result, you get a value that indicates how many turns are needed per 1 V of voltage.
For primary winding a conductor with a diameter of 2.36 mm is suitable, which needs to be folded in half. In principle, you can take any wire with a diameter of 1.5-2.5 mm. But first you need to calculate the cross-section of the conductors in the loop. First you need to wind the primary winding (220 V), and then the secondary. Its wire must be insulated along its entire length.
If you make a tap in the secondary winding in the section where 13 V is obtained and put a diode bridge, then this transformer can be used instead of a battery if you want to start the car. For welding, the voltage on the secondary winding must be in the range of 60-70 V, which will allow the use of electrodes with a diameter of 3 to 5 mm.
If you have laid both windings, and there is free space in this structure, then you can add 4 turns of a copper bus (40 x 5 mm). In this case, you will receive a spot-welding coil that will allow you to join sheet metal up to 1.5 mm thick.
For case making using metal is not recommended. It is better to make it from PCB or plastic. In the places where the coil is attached to the body, rubber gaskets should be laid to reduce vibration and better isolation from conductive materials.

Homemade spot welding machine
A ready-made device for spot welding has a rather high price, which does not justify its internal “stuffing”. It is arranged very simply, and it will not be difficult to make it yourself.

To make a spot welding machine yourself, you need one microwave transformer with a power of 700-800 watts.It is necessary to remove the secondary winding from it in the manner described above, in the section where the manufacture of a welding machine from a microwave was considered.
A spot welder is made in the following way.
- Make 2-3 turns inside the manit conductor with a cable with a conductor diameter of at least 1 cm.This will be a secondary winding that allows you to get a current of 1000 A.

- It is recommended to install copper lugs on the cable ends.

- If we connect 220 V to the primary winding, then on the secondary winding we will get a voltage of 2 V with a current strength of about 800 A. This will be enough to melt a regular nail in a few seconds.


- Followed by make a case for the device... Suitable for the base wooden plank, from which several elements are to be made, as shown in the following figure. The dimensions of all parts can be arbitrary and depend on the dimensions of the transformer.


- To give the cabinet a more aesthetic appearance, sharp corners can be removed with hand router with an edge molding cutter installed on it.


- On one part of the welding gun, cut a small wedge... Thanks to him, the ticks will be able to rise higher.


- Cut out the holes for the switch and the power cable on the back of the case.
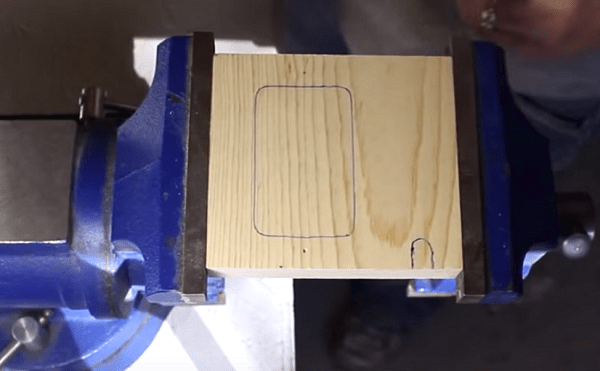
- When all the parts are ready and sanded, they can be painted with black paint or varnished.

- From an unnecessary microwave, you will need to disconnect the power cable and limit switch. You will also need a metal doorknob.


- If you do not have a switch and a copper rod or copper clamps lying around at home, then these parts must be purchased.

- Cut 2 small rods from the copper wire, which will act as electrodes, and fix them in the clamps.


- Screw the switch to the back of the device.

- Screw the back wall and 2 posts to the base, as shown in the following photos.


- Fix the transformer to the base.

- Further, one mains wire is connected to the primary winding of the transformer. The second mains wire is connected to the first terminal of the switch. Then you need to attach the wire to the second terminal of the switch and connect it to the other terminal of the primary. But a break should be made on this wire and installed in it breaker removed from the microwave... It will act as a welding start button. These wires must be long enough to accommodate the breaker at the end of the clamp.
- Attach the cover of the machine with the handle attached to the uprights and the back wall.

- Secure the side walls of the case.

- The welding gun can now be installed. First, drill at their ends along the hole into which the screws will be screwed.

- Next, attach the switch to the end.

- Insert the pliers into the housing, placing a square block between them to align. Drill holes in the pliers through the sidewalls and insert long nails into them to serve as pivots.


- Attach copper electrodes to the ends of the pliers and align them so that the ends of the rods are opposite each other.


- To make the upper electrode rise automatically, screw in 2 screws and fix the rubber band on them, as shown in the following photo.


- Switch on the unit, connect the electrodes and press the start button. You should see an electrical discharge between the copper rods.

- To check the operation of the unit, you can take metal washers and weld them.


In this case, the result was positive. Therefore, the creation of a spot welding machine can be considered complete.
It is quite possible to make a welding inverter with your own hands, even without having deep knowledge in electronics and electrical engineering, the main thing is to strictly adhere to the scheme and try to understand well how such a device works. If you make an inverter, specifications and the efficiency of which will differ little from similar parameters of serial models, you can save a decent amount.
You should not think that a home-made machine will not give you the opportunity to efficiently carry out welding work. Such a device, even assembled according to a simple scheme, will allow you to weld with electrodes with a diameter of 3-5 mm and an arc length equal to 10 mm.
Characteristics of a homemade inverter and materials for its assembly
Having assembled a welding inverter with your own hands using a fairly simple electrical circuit, you will get efficient devicewith the following technical characteristics:
- the value of the consumed voltage - 220 V;
- the strength of the current supplied to the input of the device - 32 A;
- the current generated at the output of the device is 250 A.
During operation, the diodes of such a bridge get very hot, so they must be mounted on radiators, which can be used as cooling elements from old computers. To mount the diode bridge, it is necessary to use two radiators: the upper part of the bridge through a mica gasket is attached to one radiator, the lower part through a layer of thermal paste - to the second.
The terminals of the diodes, from which the bridge is formed, must be directed in the same direction as the terminals of the transistors, with the help of which the direct current will be converted into high-frequency alternating current. The wires connecting these leads should be no longer than 15 cm. Between the power supply and the inverter unit, which is based on transistors, there is a sheet of metal, which is attached to the body of the device by welding.

Power block
The basis of the power unit of the welding inverter is a transformer, due to which the magnitude of the high-frequency current voltage decreases, and its strength increases. In order to make a transformer for such a block, it is necessary to select two cores Ш20х208 2000 nm. You can use newsprint to provide a gap between them.
The windings of such a transformer are made not of wire, but of a copper strip 0.25 mm thick and 40 mm wide.
Each layer is wrapped with tape from the cash register to ensure thermal insulation, which demonstrates good wear resistance. The secondary winding of the transformer is formed from three layers of copper strips, which are insulated with fluoroplastic tape. The characteristics of the transformer windings must correspond to the following parameters: 12 turns x 4 turns, 10 sq. mm x 30 sq. mm.
Many people try to make the windings of a step-down transformer from thick copper wire, but this is the wrong decision. Such a transformer operates on high-frequency currents, which are forced out onto the surface of the conductor without heating its inner part. That is why for the formation of windings the best option is a conductor with a large surface area, that is, a wide copper strip.

Ordinary paper can also be used as insulating material, but it is less durable than tape from a cash register. Such a tape will darken from an increased temperature, but its durability will not suffer from this.
The transformer of the power unit in the course of its operation will be very hot, therefore, for its forced cooling, it is necessary to use a cooler, which can be used as a device that was previously used in the computer's system unit.
Inverter unit
Even a simple welding inverter must fulfill its main function - to convert the direct current generated by the rectifier of such an apparatus into high frequency alternating current. To solve this problem, power transistors are used that open and close at a high frequency.
Schematic diagram of the inverter unit (click to enlarge)
The inverter unit of the device, which is responsible for converting direct current into high-frequency alternating current, is best assembled on the basis of not one powerful transistor, but several less powerful ones. Such a constructive solution will allow stabilizing the current frequency, as well as minimizing noise effects during welding.
The electronic also contains capacitors connected in series. They are needed to accomplish two main tasks:
- minimization of resonant transformer emissions;
- reducing losses in the transistor unit, arising when it is turned off and due to the fact that the transistors open much faster than they close (at this moment, current losses may occur, accompanied by heating of the keys of the transistor unit).

Cooling system
The power elements of the homemade welding inverter circuit get very hot during operation, which can lead to their failure. To prevent this from happening, in addition to the radiators on which the hottest units are mounted, it is necessary to use fans responsible for cooling.
If you have a powerful fan, you can get by with one, directing the air flow from it to a step-down power transformer. If you are using low-power fans from old computers, you will need about six of them. Simultaneously, three such fans should be installed next to the power transformer, directing the air flow from them to it.

To prevent overheating of a homemade welding inverter, you should also use a thermal sensor, installing it on the hottest radiator. Such a sensor, if the radiator reaches a critical temperature, will cut off the flow of electric current to it.
In order for the ventilation system of the inverter to work efficiently, properly designed air intakes must be present in the housing. The grilles of such intakes, through which air flows will enter the device, should not be blocked by anything.
DIY inverter assembly
For a homemade inverter device, you need to choose a reliable case or make it yourself, using sheet metal with a thickness of at least 4 mm. As the base on which the transformer of the welding inverter will be mounted, you can use a sheet of getinax with a thickness of at least 0.5 cm.The transformer itself is mounted on such a base using brackets that can be made with your own hands from copper wire with a diameter of 3 mm.

To create the electronic boards of the device, you can use a foil-clad textolite 0.5–1 mm thick. When installing magnetic cores that will heat up during operation, it is necessary to provide for the gaps between them, which are necessary for free air circulation.
For automatic control, you will need to purchase and install a PWM controller in it, which will be responsible for stabilizing the welding current and voltage. To make it convenient for you to work with your homemade device, you need to mount the controls in the front of its body. Such organs include a toggle switch for turning on the device, a variable resistor knob with which the welding current is regulated, as well as cable clamps and signal LEDs.

Diagnostics of a homemade inverter and its preparation for work
Making is half the battle. An equally important task is to prepare it for work, during which the correct functioning of all elements is checked, as well as their adjustment.
The first thing to do when testing a homemade welding inverter is to apply 15V to the PWM controller and one of the cooling fans. This will allow you to simultaneously check the functionality of the controller and avoid overheating during such a check.

After the capacitors of the device are charged, a relay is connected to the electrical supply, which is responsible for closing the resistor. If you apply voltage to the resistor directly, bypassing the relay, an explosion can occur. After the relay is activated, which should happen within 2-10 seconds after the voltage is applied to the PWM controller, it is necessary to check if the resistor has shorted.
When the relays of the electronic circuit are triggered, rectangular pulses should form on the PWM board, going to the optocouplers. This can be checked using an oscilloscope. The correct assembly of the diode bridge of the device must also be checked; for this, a voltage of 15 V is applied to it (the current strength should not exceed 100 mA).
The phases of the transformer during the assembly of the device may have been incorrectly connected, which can lead to incorrect operation of the inverter and the generation of loud noises. To prevent this from happening, the correctness of the phase connection must be checked; for this, a two-beam oscilloscope is used. One beam of the device is connected to the primary winding, the second to the secondary. The phases of the pulses, if the windings are connected correctly, should be the same.

The correct manufacture and connection of the transformer is checked using an oscilloscope and connecting electrical devices with different resistances to the diode bridge. Focusing on the noise of the transformer and the oscilloscope readings, they conclude that it is necessary to modify the electronic circuit of the homemade inverter apparatus.
To check how much you can continuously work on a homemade inverter, you need to start testing it from 10 seconds. If the radiators of the device do not heat up during this duration, you can increase the period to 20 seconds. If such a time period did not negatively affect the state of the inverter, you can increase the operating time of the welding machine up to 1 minute.
Maintenance of a homemade welding inverter
In order for the inverter apparatus to serve for a long time, it must be properly maintained.
In the event that your inverter stops working, you need to open its cover and blow out the insides with a vacuum cleaner. Where dust remains can be thoroughly cleaned with a brush and dry cloth.
The first thing to do when diagnosing the welding inverter is to check the voltage supply to its input. If the voltage is not supplied, the power supply should be diagnosed. The problem in this situation may also be that the fuses on the welding machine have blown. Another weak link of the inverter is the temperature sensor, which, in the event of a breakdown, should not be repaired, but replaced.

When performing diagnostics, it is necessary to pay attention to the quality of the connections of the electronic components of the device. Determine poorly made connections visually or using a tester. If such connections are identified, they must be corrected so as not to face further overheating and failure of the welding inverter.
Only if you pay due attention to the maintenance of the inverter device, you can count on the fact that it will serve you for a long time and will enable you to perform welding work as efficiently and efficiently as possible.
5, average rating: 3,20
out of 5)
Figure 1. Diagram of a bridge rectifier for a welding machine.
Welding machines are available in DC and AC.
S.A. direct current are used when welding at low currents of thin sheet metal (roofing steel, automobile, etc.). DC arc is more stable, direct and reverse polarity can be welded. On direct current, you can weld with electrode wire without coating and electrodes intended for welding, both on direct current and on alternating current. To give stability to arc burning at low currents, it is desirable to have an increased open-circuit voltage Uxx of the welding winding (up to 70 - 75 V). For the rectification of alternating current, the simplest "bridge" rectifiers on powerful diodes with cooling radiators are used (Fig. 1).
To smooth out voltage ripples, one of S.A. A is connected to the electrode holder through a choke L1, which is a coil of 10-15 turns of a copper bus with a cross section of S \u003d 35 mm 2, wound on any core, for example, from. For straightening and smooth regulation of the welding current, more complex circuits are used with the use of powerful controlled thyristors. One of the possible circuits on thyristors of the T161 (T160) type is given in the article by A. Chernov "Both will charge and weld" (Modelist-constructor, 1994, No. 9). The advantages of DC regulators are their versatility. The range of voltage variation by them is 0.1-0.9 Uxx, which makes it possible to use them not only for smooth adjustment of the welding current, but also for charging storage batteries, powering electric heating elements and other purposes.

Figure 2. Diagram of the falling external characteristics of the welding machine.
Figure: 1. Bridge rectifier for the welding machine. Shown connection S.A. for welding thin sheet metal on "reverse" polarity - "+" on the electrode, "-" on the workpiece to be welded U2: - output alternating voltage of the welding machine
AC welding machines are used for welding with electrodes, the diameter of which is more than 1.6 - 2 mm, and the thickness of the products to be welded is more than 1.5 mm. In this case, the welding current is significant (tens of amperes) and the arc burns quite steadily. The electrodes used are intended for welding only on alternating current. For normal operation of the welding machine, you must:
- Provide output voltage for reliable arc ignition. For amateur S.A. Uxx \u003d 60 - 65v. A higher open-circuit output voltage is not recommended, which is mainly associated with ensuring operational safety (Uxx industrial welding machines - up to 70 - 75 V).
- Provide welding voltage Uw, required for stable arc burning. Depending on the diameter of the electrode - Uw \u003d 18 - 24v.
- Provide rated welding current Iw \u003d (30 - 40) de, where Iw is the value of the welding current, A; 30 - 40 - coefficient depending on the type and diameter of the electrode; de - electrode diameter, mm.
- Limit the short-circuit current Isc, the value of which should not exceed the rated welding current by more than 30 - 35%.
Stable arc burning is possible if the welding machine has a falling external characteristic, which determines the relationship between the current and voltage in the welding circuit (Fig. 2).
S.A. shows that for a rough (stepwise) overlap of the range of welding currents, it is necessary to switch both primary windings and secondary windings (which is structurally more difficult due to the large current flowing in it). In addition, mechanical devices for moving the windings are used to smoothly change the welding current within the selected range. When removing the welding winding relative to the mains, magnetic leakage fluxes increase, which leads to a decrease in the welding current.

Figure 3. Diagram of a rod-type magnetic circuit.
When designing an amateur SA, one should not strive to completely cover the range of welding currents. It is advisable at the first stage to assemble a welding machine for working with electrodes with a diameter of 2 - 4 mm, and at the second stage, if it is necessary to work at low welding currents, to supplement it with a separate rectifier device with smooth regulation of the welding current. Amateur welding machines must meet a number of requirements, the main of which are the following: relative compactness and low weight; sufficient duration of operation (at least 5 - 7 electrodes de \u003d 3 - 4 mm) from the 220V network.
The weight and dimensions of the apparatus can be reduced due to a decrease in its power, and an increase in the duration of operation - due to the use of steel with high magnetic permeability and heat-resistant insulation of the winding wires. These requirements are easy to fulfill, knowing the basics of designing welding machines and adhering to the proposed technology for their manufacture.
Figure: 2. Falling external characteristic of the welding machine: 1 - a family of characteristics for different ranges of welding; Iw2, Iwz, Iw4 - ranges of welding currents for electrodes with a diameter of 2, 3 and 4 mm, respectively; Uxx - open circuit voltage CA. Ikz - short-circuit current; Ucv - welding voltage range (18 - 24 V).
Figure: 3. Rod-type magnetic circuit: a - L-shaped plates; b - U-shaped plates; c - plates made of strips of transformer steel; S \u003d axb- cross-sectional area of \u200b\u200bthe core (core), cm 2 s, d- window dimensions, see.
So, the choice of the type of core. For the manufacture of welding machines, mainly rod-type magnetic cores are used, since they are more technological in design. The core is recruited from plates of electrical steel of any configuration with a thickness of 0.35-0.55 mm, tightened with studs isolated from the core (Fig. 3). When selecting a core, it is necessary to take into account the dimensions of the "window" to accommodate the windings of the welding machine, and the cross-sectional area of \u200b\u200bthe core (core) S \u003d axb, cm 2. As practice shows, one should not choose the minimum values \u200b\u200bof S \u003d 25 - 35 cm, since the welding machine will not have the required power reserve and it will be difficult to obtain high-quality welding. And overheating of the welding machine after a short time is also inevitable.

Figure 4. Diagram of a toroidal magnetic circuit.
The cross section of the core should be S \u003d 45 - 55 cm 2. The welding machine will be somewhat heavier, but will not let you down! Amateur welding machines on toroidal cores, which have higher electrical characteristics, are about 4 - 5 times higher than those of a rod, and the electrical losses are small, are becoming more and more widespread. The labor costs for their manufacture are more significant and are primarily associated with the placement of the windings on the torus and the complexity of the winding itself.
However, with the right approach, they give good results. The cores are made of tape transformer iron rolled into a torus-shaped roll. An example is a core made of an autotransformer "Latr" for 9 A. To increase the inner diameter of the torus ("window"), a part of the steel tape is unwound from the inside and wound onto the outer side of the core. But, as practice shows, "Latra" alone is not enough to produce high-quality SA. (small cross section S). Even after working with 1 - 2 electrodes with a diameter of 3 mm, it overheats. It is possible to use two similar cores according to the scheme described in B. Sokolov's article "Welding baby" (Sam, 1993, No. 1), or to manufacture one core by rewinding two (Fig. 4).
Figure: 4. Toroidal magnetic circuit: 1.2 - autotransformer core before and after rewinding; 3 design by S.A. based on two toroidal cores; W1 1 W1 2 - mains windings connected in parallel; W 2 - welding winding; S \u003d axb- core cross-sectional area, cm 2, s, d- inner and outer torus diameters, cm; 4 - electrical circuit S.A. based on two joined toroidal cores.
Special attention should be paid to amateur SA, made on the basis of stators of asynchronous three-phase electric motors of high power (more than 10 kW). The choice of the core is determined by the cross-sectional area of \u200b\u200bthe stator S. The stamped stator plates do not fully correspond to the parameters of electrical transformer steel, therefore, it is inappropriate to reduce the cross-section S below 40 - 45 cm.

Figure 5. Scheme of fastening the conclusions of the CA windings.
The stator is freed from the housing, the stator windings are removed from the inner grooves, the groove bridges are cut with a chisel, the inner surface is protected with a file or an abrasive wheel, the sharp edges of the core are rounded and wrapped tightly, overlapping with cotton insulating tape. The core is now ready for winding.
Choice of windings. For primary (network) windings, it is better to use a special copper winding wire in h.b. (fiberglass) insulation. Wires in rubber or rubber-fabric insulation also have satisfactory heat resistance. Unsuitable for work at elevated temperatures (and this is already incorporated into the design of an amateur SA) wires in polyvinyl chloride (PVC) insulation due to its possible melting, leakage from the windings and their short circuit. Therefore, PVC insulation from the wires must either be removed and wrapped along the entire length of the h.b. with insulating tape, or do not remove, but wrap the wire over the insulation. Another proven winding method is also possible. But more on that below.
When selecting the cross-section of the winding wires, taking into account the specifics of S.A. (periodic) we assume a current density of 5 A / mm 2. At a welding current of 130 - 160 A (electrode de \u003d 4 mm), the power of the secondary winding will be P 2 \u003d Iw x 160x24 \u003d 3.5 - 4 kW, the power of the primary winding, taking into account losses, will be about 5 - 5.5 kW, and therefore the maximum current of the primary winding can reach 25 A. Therefore, the cross-section of the wire of the primary winding S 1 must be at least 5 - 6 mm. In practice, it is advisable to use a wire with a cross section of 6 - 7 mm 2. Either it is a rectangular bus, or a copper winding wire with a diameter (without insulation) of 2.6 - 3 mm. (Calculation according to the well-known formula S \u003d piR 2, where S is the area of \u200b\u200bthe circle, mm 2 pi \u003d 3.1428; R is the radius of the circle, mm.) If the section of one wire is insufficient, winding in two is possible. When using an aluminum wire, its cross section must be increased by 1.6 - 1.7 times. Is it possible to reduce the cross-section of the mains winding wire? Yes, you can. But at the same time S.A. will lose the required power reserve, it will heat up faster, and the recommended core section S \u003d 45 - 55 cm in this case will be unjustifiably large. The number of turns of the primary winding W 1 is determined from the following ratio: W 1 \u003d [(30 - 50): S] x U 1 where 30-50 is a constant coefficient; S - core section, cm 2, W 1 \u003d 240 turns with taps from 165, 190 and 215 turns, i.e. every 25 turns.

Figure 6. Diagram of ways of winding CA windings on a rod-type core.
A larger number of network winding taps, as practice shows, is impractical. And that's why. Due to a decrease in the number of turns of the primary winding, both the power of SA and Uxx increase, which leads to an increase in the arc voltage and a deterioration in the quality of welding. Consequently, it is impossible to achieve overlapping of the range of welding currents only by changing the number of turns of the primary winding without deteriorating the quality of welding. For this, it is necessary to provide for switching the turns of the secondary (welding) winding W 2.
The secondary winding W 2 must contain 65 - 70 turns of an insulated copper bus with a cross section of at least 25 mm (preferably a cross section of 35 mm). Flexible stranded wire (for example, welding wire) and three-phase power stranded cable are also quite suitable. The main thing is that the cross-section of the power winding should not be less than the required one, and the insulation should be heat-resistant and reliable. With insufficient wire cross-section, winding in two or even three wires is possible. When using an aluminum wire, its cross section must be increased by 1.6 - 1.7 times.
Figure: 5. Fastening of the CA winding leads: 1 - CA case; 2 - washers; 3 - terminal bolt; 4 - nut; 5 - copper tip with a wire.
The difficulty of acquiring switches for high currents, and practice shows that it is most simple to lead the leads of the welding winding through copper lugs under terminal bolts with a diameter of 8-10 mm (Fig. 5). Copper lugs are made from copper tubes of a suitable diameter, 25-30 mm long, and fixed on the wires by crimping and preferably soldering. Let's pay special attention to the order of winding winding. General rules:
- Winding should be done on an isolated core and always in one direction (eg clockwise).
- Each layer of the winding is insulated with a layer of h.b. insulation (fiberglass, electrical cardboard, tracing paper), preferably impregnated with bakelite varnish.
- The conclusions of the windings are tinned, marked, fixed with h.b. braid, on the conclusions of the network winding, they additionally put on h.b. cambric.
- In case of doubts about the quality of insulation, winding can be carried out using a cotton cord, as it were, in two wires (the author used a cotton thread for fishing). After winding one layer, the winding with h.b. thread is fixed with glue, varnish, etc. and after drying, the next row is wound.

Figure 7. Diagram of ways of winding CA windings on a toroidal core.
Consider the order of arrangement of the windings on a rod-type magnetic circuit. The mains winding can be positioned in two main ways. The first method allows you to get a more "hard" welding mode. The mains winding in this case consists of two identical windings W 1 W 2 located on different sides of the core, connected in series and having the same wire cross-section. To adjust the output current, taps are made on each of the windings, which are closed in pairs (Fig. 6a, c).
The second method involves winding the primary (mains) winding on one of the sides of the core (Fig. 6 c, d). In this case, the CA has a steeply dipping characteristic, it cooks "softly", the arc length has less effect on the value of the welding current, and, consequently, on the quality of welding. After winding the primary winding of the CA, it is necessary to check for the presence of short-circuited turns and the correctness of the selected number of turns. The welding transformer is connected to the network through a fuse (4 - 6A) and preferably an alternating current ammeter. If the fuse burns out or gets very hot, then this is a clear sign of a short-circuited loop. Consequently, the primary winding will have to be rewound, paying particular attention to the quality of the insulation.
Figure: 6. Methods of winding CA windings on a rod-type core: a - mains winding on both sides of the core; b - the corresponding secondary (welding) winding, connected in counter-parallel; c - mains winding on one side of the core; d - the corresponding secondary winding, connected in series.
If the welding machine hums strongly, and the current consumption exceeds 2 - 3 A, then this means that the number of the primary winding is underestimated and it is necessary to wind up a certain number of turns. A serviceable AC consumes no more than 1 - 1.5 A no-load current, does not heat up and does not buzz much. The secondary winding CA is always wound on both sides of the core. For the first method of winding, the secondary winding also consists of two identical halves, included to increase the stability of arc burning (Fig. 6) counter-parallel, and the wire cross-section can be taken slightly less - 15 - 20 mm 2.

Figure 8. Connection diagram of measuring devices.
For the second method of winding, the main welding winding W 2 1 is wound on the side of the core free from windings and is 60 - 65% of the total number of turns of the secondary winding. It serves mainly to ignite the arc, and during welding, due to a sharp increase in the magnetic leakage flux, the voltage across it drops by 80 - 90%. An additional welding winding W 2 2 is wound over the primary. Being power, it maintains the welding voltage, and therefore the welding current, within the required limits. The voltage across it drops in welding mode by 20 - 25% relative to the open circuit voltage. After the manufacture of S.A, it is necessary to adjust it and check the quality of welding with electrodes of various diameters. The setup process is as follows. To measure the welding current and voltage, it is necessary to purchase two electrical measuring devices - an AC ammeter for 180-200 A and an AC voltmeter for 70-80 V.
Figure: 7. Methods of winding CA windings on a toroidal core: 1.2 - uniform and sectional winding of the windings, respectively: a - network b - power.
Their connection diagram is shown in Fig. 8. When welding with different electrodes, the values \u200b\u200bof the welding current - Iw and the welding voltage Uw, which must be within the required limits, are removed. If the welding current is small, which happens most often (the electrode sticks, the arc is unstable), then either by switching the primary and secondary windings, the required values \u200b\u200bare set, or the number of turns of the secondary winding is redistributed (without increasing them) in the direction of increasing the number of turns wound over network winding. After welding, you can make a break or sawing the edges of the welded products, and the quality of the welding becomes immediately clear: the penetration depth and the thickness of the deposited metal layer. It is useful to draw up a table based on the measurement results.

Figure 9. Diagram of welding voltage and current meters and current transformer design.
Based on the data in the table, the optimal welding modes are selected for electrodes of various diameters, keeping in mind that when welding with electrodes, for example, 3 mm in diameter, electrodes with a diameter of 2 mm can be cut, because cutting current is higher than welding current by 30 -25%. The difficulty of purchasing the measuring devices recommended above forced the author to start making a measuring circuit (Fig. 9) based on the most common DC milliammeter at 1-10 mA. It consists of voltage and current meters assembled in a bridge circuit.
Figure: 9. Schematic diagram of welding voltage and current meters and current transformer design.
The voltage meter is connected to the output (welding) winding of S.A. Adjustment is carried out using any tester that monitors the welding output voltage. With the help of variable resistance R.3, the arrow of the device is set to the final division of the scale at the maximum value Uxx The scale of the voltage meter is quite linear. For greater accuracy, you can take two or three test points and calibrate the measuring device to measure voltages.
It is more difficult to set up a current meter as it connects to a self-made current transformer. The latter is a toroidal core with two windings. The dimensions of the core (outer diameter 35-40 mm) are not of fundamental importance, the main thing is that the windings fit. The core material is transformer steel, permalloy or ferrite. The secondary winding consists of 600 - 700 turns of PEL, PEV insulated copper wire, better than PELSHO with a diameter of 0.2 - 0.25 mm and is connected to a current meter. The primary winding is the power wire that runs inside the ring and connects to the terminal bolt (fig. 9). Setting up a current meter is as follows. To the power (welding) winding S.A. connect a calibrated resistance from a thick nichrome wire for 1 - 2 seconds (it gets very hot) and measure the voltage at the output of S.A. By determining the current flowing in the welding winding. For example, when connecting Rн \u003d 0.2 ohm, Uout \u003d 30v.

A point is marked on the scale of the instrument. Three to four measurements with different R H are enough to calibrate the current meter. After calibration, the instruments are installed on the S.A case, using generally accepted recommendations. When welding in different conditions (strong or low-current network, long or short supply cable, its cross-section, etc.) by switching the windings, set up S.A. to the optimal welding mode, and then the switch can be set to the neutral position. A few words about contact spot welding. To the design of S.A. This type has a number of specific requirements:
- The power delivered at the time of welding should be maximum, but not more than 5-5.5 kW. In this case, the current consumed from the network will not exceed 25 A.
- The welding mode must be "hard", and, consequently, the winding of SA windings. should be carried out according to the first option.
- The currents flowing in the welding winding reach values \u200b\u200bof 1500-2000 A and above. Therefore, the welding voltage should be no more than 2-2.5v, and the open circuit voltage should be 6-10v.
- The cross-section of the wires of the primary winding is at least 6-7 mm, and the cross-section of the secondary winding is at least 200 mm. This wire cross-section is achieved by winding 4-6 windings and their subsequent parallel connection.
- Additional taps from the primary and secondary windings are impractical.
- The number of turns of the primary winding can be taken as the minimum calculated due to the short duration of S.A.
- It is not recommended to take a section of the core (core) less than 45-50 cm.
- Welding lugs and submarine cables to them must be copper and carry the appropriate currents (lug diameter 12-14 mm).

A special class of amateur S.A. represent devices made on the basis of industrial lighting and other transformers (2-3 phase) for an output voltage of 36V and a power of at least 2.5-3 kW. But before taking on the alteration, it is necessary to measure the core cross-section, which should be at least 25 cm, and the diameters of the primary and secondary windings. It will immediately become clear to you what can be expected from the alteration of this transformer.
And finally, a few technology tips.
The connection of the welding machine to the network should be made with a wire with a cross section of 6-7 mm through an automatic machine for a current of 25-50 A, for example AP-50. The diameter of the electrode, depending on the thickness of the welded metal, can be selected based on the following ratio: da \u003d (1-1.5) L, where L is the thickness of the welded metal, mm.
The length of the arc is chosen depending on the diameter of the electrode and is on average 0.5-1.1 d3. It is recommended to perform welding with a short arc of 2-3 mm, the voltage of which is 18-24 V. An increase in the arc length leads to a violation of the stability of its combustion, an increase in losses for waste and spatter, and a decrease in the depth of penetration of the base metal. The longer the arc, the higher the welding voltage. The welding speed is chosen by the welder depending on the grade and thickness of the metal.

When welding on straight polarity, the plus (anode) is connected to the workpiece and the minus (cathode) to the electrode. If it is necessary that less heat is generated on the part, for example, when welding thin-sheet structures, welding is used in reverse polarity (Fig. 1). In this case, the minus (cathode) is attached to the workpiece to be welded, and the plus (anode) is attached to the electrode. In this case, not only is less heating of the workpiece being welded, but the process of melting the electrode metal is accelerated due to more high temperature anode zone and greater heat input.
Welding wires are connected to the CA through copper lugs for terminal bolts on the outside of the welding machine body. Poor contact connections reduce the power characteristics of the CA, deteriorate the quality of welding and can cause them to overheat and even fire the wires. With a short length of welding wires (4-6 m), their cross-section should be at least 25 mm. When performing welding work, it is necessary to observe the rules of fire and electrical safety when working with electrical appliances.
Welding work should be carried out in a special mask with C5 protective glass (for currents up to 150-160 A) and gloves. All switching of the CA should be performed only after disconnecting the welding machine from the mains.
It makes sense to independently manufacture a welding machine in the case when it is necessary to perform relatively small amounts of welding work in a domestic environment. Knowing the basic principles of the device, you can assemble it from readily available parts and materials.
First of all, it is worth determining how much power the welding current will be required in the work. Obviously, for processing thin metal sheets up to 2 mm, a much lower current intensity is needed than for massive reinforcement. Depending on these characteristics of the material, the diameter of the electrode is selected. For workpieces up to 2 mm thick, an electrode 1.5 - 3 mm in diameter is suitable. Accordingly, for parts 3-5 mm - electrode 3-4 mm, parts up to 10 mm - electrode 4-5 mm, parts up to 24 mm - electrode 5-6 mm and parts up to 60 mm - electrode 6-8 mm. Having determined the diameter of the electrode, we select the required value of the welding current. For electrodes with a diameter of up to 1.5 mm, a welding current of 4o A, 2 mm - 70 A, 3 mm - up to 140 A, 4 mm - up to 200 A.



A welding machine made independently using carefully selected components can fully replace an expensive finished machine and reliably serve the owner for many years.



