Innovative products in tourism are an example. Modern trends in the development of innovative types of tourism. Information technologies, their implementation in production processes
What types of innovations are typical for tourism activities?
Russia, according to a study by the World Tourism Organization and the World Tourism Council, ranks 68th in the world tourism market in terms of competitiveness. In the modern "knowledge economy", competitiveness is associated with the ability to develop and propose innovations in accordance with new trends in the demand for tourism products.
Economic science confidently refers to innovative trends in the production of tourist products only trends in e-tourism (development of electronic offer of tourist services, advertising, other marketing communications, sales via the Internet). Researchers agree that tourism is an active consumer of technical innovations from other industries; but the question of whether the enterprises of the tourism industry produce innovations on their own and what is considered an innovation in tourism remains controversial. To the problem of defining innovation in tourism, scientific approaches are only being sought. A patent search showed that there were only 254 tourism patents registered worldwide; however, only software products or new products for tourism were patented. Other types of innovations in tourism are not patented.
Innovation in tourism "involves the development of an original approach, the development of new ways to use existing resources while looking for the development of new resources." The typification of innovation in tourism was developed by Abernathy and Clark, who distinguish 4 types of innovation: regular, niche, revolutionary and architectural.
Regular innovation refers to the continuous improvement of the quality of services, staff development and labor productivity.
Niche innovation usually changes collaboration structures, but not basic knowledge and skills; they combine existing services in new ways.
Revolutionary innovation is associated with the use of new technologies in firms, the development of new methods; they radically influence the key knowledge and skills of personnel up to the emergence of new professions in the sector.
Architectural innovation is changing the structures, business models and rules in tourism; they create new events and objects that require reorganization, change the physical or institutional infrastructure, research and training base.
What types of innovations exist in tourism?
1. Product innovation - the introduction of a new product (tour, service, product) into the tourist market. Its novelty should be obvious to manufacturers, suppliers, consumers and competitors.
For example, offering the market a new event - a festival, forum, fashion show or costume performance; or a new tour, such as a food tour of national cuisine. New services in recent years are accommodation in environmentally friendly accommodations, virtual tours of museums. Product innovations (patented) include, for example, a mini submarine for tourism, an electronic travel guide, special hiking boots with integrated lighting and electronics.
2. Process innovation - the introduction of new or significantly improved techniques and technologies in the process of providing a service (complex of services). Can be combined with product innovation.
For example, cleaning robots, computer tracking systems, integrated hotel management systems, automated booking and sales of airline tickets, electronic ticketing.
- 3. Innovation in management - the introduction of more efficient structures and procedures for organizing the firm's activities, cooperation systems, new job profiles and professional requirements. Management innovation is often combined with process innovation.
- 4. Business model innovation - new ways of doing business that increase its value and value for the consumer; development of new approaches in the relationship between the client and the firm, between the firms-producers of services.
For example, the creation of customer databases and data banks in hotels, which allows an individual approach to service. Or the entry of a national airline into a global alliance to optimize transportation. A new business model in Russia is a system of mutual settlements for tourist services in terms of the implementation of tours, spa and wellness services through the Transport Clearing House.
- 5. Marketing innovation - the development of new marketing approaches with improvements in pricing, offer, promotion, payment for a tourist product. For example, preferential pricing for regular customers of airlines or an all-inclusive sales system.
- 6. Innovation in logistics - new solutions in systems and chains of supply, distribution, delivery, including tourists.
Recent innovations in this area are airport hub systems - a fundamentally new concept of moving through a single air transport hub; integrated information systems of destinations; clearing system for mutual settlements in air transport.
7. Institutional innovations - form new rules and regulatory systems in tourism, as well as industries serving tourists; create new systems and forms of cooperation between the administration, the private sector and the public in tourist areas.
For example, changes in the Law "On special economic zones in the Russian Federation" and the creation of zones of a tourist and recreational type; RF Law "On state regulation of activities related to the organization and conduct of gambling" and gambling zones; amendments to the Federal Law "On the Basics of Tourist Activity in the Russian Federation", introducing a mechanism for the financial responsibility of tour operators - institutional innovations.
8. Resource innovation - the use of a new type of resources for the organization of tourism and the development of new tours and services. The tourism sector is starting to actively incorporate new resources into its economy and use them to create a new supply.
For example, the excavation of dinosaur remains formed the basis of the Dinosor Tourist Park in the United States, with a paleontological museum and routes showing archaeological findings. The opal mines and mining community in Coober Pedy, Australia is another example of a new resource used to develop a tour. The city of giant pandas is being built for tourists in China. In Evenkia, an open-air museum dedicated to the fall of the Tunguska meteorite and the Leonid Kulik trail route, along which the first explorer of the meteorite in the 1920s walked through the swamps and taiga from the village of Vanavara to the place of the fall of the cosmic body, was created.
9. Conceptual innovations - the creation of new concepts of tourism, tourist services, and their implementation in new service formats, new architectural, engineering and technological solutions that meet the needs of tourists.
Conceptual innovations include, for example, the construction of hotels and restaurants made of ice in the Nordic countries (the most famous is the Ice Hotel in Sweden), the concept of themed casino hotels in Las Vegas (for example, Excalibur, a medieval castle where knights tournaments).
These types of innovations satisfy the need for new knowledge, new experience, which is typical for modern tourists seeking self-development through travel and tourism.
Tourism is a fairly important area in the global economy. Many states allocate it as the main source of income, and quite profitable. More and more people travel in their free time, wanting to see the world. To do this, there is a wide range of programs that agencies offer. in tourism, of course, they do not stand still.
The introduction of innovations and the ability to manage them are important points in the development of this area. When choosing a vacation spot, a traveler can stay in or in a bustling metropolis; there are quite a few options offered by travel agencies. Innovation in tourism is an important point that will help the client decide both in which agency to contact and in which direction to choose.
Interaction of several structures at once plays a huge role in the development of the industry. B appears most clearly. Indeed, in order to organize a quality vacation, efforts of local authorities, hotel owners, companies, etc. are required. The term "innovation in tourism" implies some principles that will lead to a better development of the industry. Also, this phrase means directions in which there is a certain novelty.

New ideas in the tourism business are a great way to grow it and increase its income. The goods that tour operators can offer are unexplored places and destinations. However, most companies are afraid to become pioneers and continue to work according to the old scheme, receiving albeit small, but stable income. At the same time, innovations in tourism can greatly facilitate work by automating some actions, increasing the flow of customers and much more. For example, an online service allows travelers to choose a route, book a hotel they like, order tickets without leaving home. Currently, more and more tourists choose this method of communicating with tour operators.

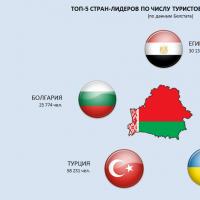
In this area, they help support the business and prevent aging of the proposed product. Turkey and Egypt are prime examples of countries that are constantly innovating in tourism. Hotels in these countries are distinguished by original design and high quality of service. At the same time, the establishments do not stand still, constantly updating the services offered.
The main goals pursued by innovation in tourism are the ability to respond to changes in the industry, as well as the continuous improvement of product quality. Offering new routes to travelers, though associated with certain risks, can, in most cases, be profitable. Competition in business is quite high, so it is quite difficult for small agencies to “stay afloat”. In order not only to maintain, but also to strengthen its position, innovations in work are needed to attract new customers.
The ability to interest travelers in their activities is a guarantee of stable income and business development. Perhaps this is only by applying innovations that will set the company apart from others.
Introduction
Innovation and tourism
1 The concept of "innovation", types and functions of innovation
Innovative activities in tourism
State support for innovation in tourism
Conclusion
List of references
Introduction
Russia is taking active steps to transition to an innovative way of economic development. Innovation is something other than actions to implement the achievements of science and technology in technology and management, including in the social sphere, i.e. in organizations that provide services to the public.
During the second half of the twentieth century. there is an acceleration in the pace of innovation and growth in the scale of innovation in all sectors of the economy, including social and cultural services and tourism.
Tourism is one of the leading and most dynamic sectors of the economy and for its rapid pace it is recognized as the economic phenomenon of the century. For 38% of countries, tourism is the main source of income, and for 83% of countries, tourism is one of the five main sources of income.
Tourism, being at present a global socio-economic phenomenon, functioning in the conditions of sometimes very tough competition, is characterized by a high degree of susceptibility to innovative processes, the adherence to which is often the main factor determining the competitiveness of tourism organizations.
The state should focus its efforts and available free resources on the development of knowledge-intensive industries that are promising for the entire national economy, i.e. such industries that actively influence and contribute to the development of other sectors of the economy. And tourism is such an industry.
1. Innovation and Tourism
1 The concept of "innovation", types and functions of innovation
Innovation and innovation activities are traditionally presented as a direction of scientific and technological progress (its high-tech component) and as a process associated with the implementation of research and development results into practice. However, the meaning and content of the concept of "innovation" is broader. The scope of innovation is comprehensive, it not only covers the practical use of scientific and technical developments and inventions, but also includes changes in the product, processes, marketing, organization. Innovation acts as an obvious factor of change, as a result of activity, embodied in a new or improved product, technological processes, new services and new approaches to meeting social needs.
The term "innovation" (from the eng. Innovation-innovation) characterizes the qualitative changes in the production process. Despite the fact that the concept of "innovation" is widely used, there is still no generally accepted definition of it. Various authors, mainly foreign (P. Drucker, N. Monchev, E. Mansfield, I. Perlaki, M. Porter, J. Schumpeter, etc.), interpret it depending on the object and subject of research - as a result and as a process ...
So, in the modern dictionary of foreign words (in accordance with the set of international standards "Frascati Guide"), innovation is the end result of innovation, embodied in the form of a new or improved product introduced on the market, a new or improved technological process used in practice or a new approach to social services.
The Oxford Explanatory Dictionary explains innovation as follows: "Any new approach to the design, manufacture, or marketing of a product that gives the innovator or his company an advantage over the competition."
The term “innovation”, in its modern sense, was first used by J. Schumpeter, who emphasized that innovation is a significant change in the function of the produced, consisting in a new combination and commercialization of all new combinations based on the use of new materials and components, the introduction of new processes , opening new markets, introducing new organizational forms.
Innovations (innovations) are possible in all areas of human activity. Based on the multivariate possibilities, innovations differ in the scope of application, the scale of distribution and in nature. In terms of application, innovations are subdivided into scientific and technical, organizational and economic, socio-cultural and state-legal. In terms of the scale of distribution, they distinguish between global, national, regional, sectoral and local (at the enterprise, company) innovations. They can be evolutionary and radical in nature.
The main functions of innovation:
they involve new productive forces in production, contribute to an increase in labor productivity and production efficiency, and reduce various kinds of costs;
raise the standard of living of each person and society as a whole due to the variety and quality of products and services produced, meeting the needs of the population;
help to bring the structure of production into line with the structure of changed needs, help maintain a balance between demand and supply, between production and consumption;
are the result of the application of the creative capabilities and knowledge of a specific person, human intelligence, which, in turn, stimulates the further growth of creative activity.
2 The essence and basic principles of innovation in tourism
The study of trends and patterns of integrated development of innovations, planning and managing positive results is a complex methodological problem in the field of tourism, associated primarily with the classification of innovations. The following classification features are distinguished as significant for determining the essence of innovation in tourism:
source of ideas (needs of tourists, discoveries, inventions);
type of innovation (attractors, tourism infrastructure, tourism products, methods and means of distribution of tourism products / services, management, factors of production);
the degree of novelty (improving, breakthrough);
breadth of impact, scale, connectivity (local, global, systemic);
investment content (non-capital-intensive, low-capital-intensive, capital-intensive).
Innovations in tourism should be considered as systemic events that have a qualitative novelty and lead to positive shifts that ensure the sustainable functioning and development of the industry in the region. So, the idea of \u200b\u200bcreating and implementing tourism projects that do not even bring significant profits at first, can give an impetus to the development of tourism and thereby actively contribute to the creation of additional jobs and an increase in the income of the population. A striking proof of this is the success of the city of Veliky Ustyug in the Vologda Region, which today positions itself as the birthplace of the Russian Father Frost and is experiencing a real tourist boom.
The innovation process in tourism is quite specific. It receives, as a rule, its recognition, on the one hand, through the tourism market and the degree of customer satisfaction, and on the other hand, mainly due to the adoption of joint decisions by tourism organizations, industry governing bodies in the region, local governments and public organizations whose activities associated with tourism, as well as due to the assessment of the industry by the local population. Only such interaction of all elements (subjects and objects) of the innovation process can lead to the emergence of a significant synergistic effect, expressed as the growth (development) of the tourism sector. The complexity and transformability of discoveries, when the introduction of a new one in one area gives an effect (and perhaps stronger) in another, which is their essence in the industry, therefore they need a scientifically based organization and management.
The main principles of innovation in tourism include:
The scientific principle, which is to use scientific knowledge and methods to implement innovations that meet the needs of tourists.
The principle of consistency. The developed strategy for the innovative development of the tourism sector in the region should take into account the factors and conditions necessary to meet the needs of people in recreation; resource opportunities of the region (economic, financial, personnel and others); social impact on society; environmental factors.
The principle of matching innovation to the needs of tourists. Only those innovations are offered that are really needed by the client, and not those that can be produced and implemented by a tourist organization.
The principle of positive results, which consists in preventing unreasonable, ill-considered creation and implementation of an innovation, which can be dangerous, firstly, for a tourist; secondly, for a specific enterprise; thirdly, for the biosphere and society as a whole.
The principle of immanence to investment processes. To carry out the necessary research, development and materialization of innovations, investment resources are used, the effectiveness of which is determined by the degree of significance and scale of innovations.
Correspondence of innovative activity and its results (innovations) to the level of development of society.
The principle of connectivity. The process of innovation ends with the appearance on the market of a product, which should, at a certain stage of its life cycle, cause a need (stimulate an idea) to create the next innovation and provide financial support for this process.
Security principle. Any innovation must ensure that there is no harm to humans and the environment.
2. Innovative activity in tourism
Innovation activity is a complex of scientific, technological, organizational, financial, commercial activities that lead to innovation. An activity is innovative if new knowledge, technologies, techniques, approaches are brought into it to obtain a result that is widely in demand in society. The innovative activity of an enterprise can be defined as the joint work of all employees aimed at creating and introducing an innovation. Innovation activity is systemic in nature, the system is formed by society and the subjects of innovation.
Key areas of innovation in tourism and hospitality:
release of new types of tourism products, restaurant products, hotel services, etc .;
the use of new equipment and technology in the production of traditional products;
the use of new tourist resources that were not previously used. A unique example is the travel of tourists on spaceships;
changes in the organization of production and consumption of traditional tourist, restaurant products, hotel services, etc .; new marketing, new management;
identification and use of new markets for products (hotel and restaurant chains).
The basis of innovation in all sectors of the economy is the implementation of the achievements of scientific and technological progress. The foregoing fully applies to the field of social and cultural services and tourism.
The scientific and technological revolution has not only become the material basis for the formation of mass tourism. It has had a huge impact on innovation in social and cultural services and tourism through high technologies, which include new materials, microprocessor technology, media and communications, biotechnology.
The emergence of polymer, composite and other new materials has led to the emergence of new types of clothing and footwear, new sports and other equipment, new containers and packaging, etc. New materials became the material basis of extreme tourism, contributed to the development of water, mountain and a number of other types of tourism.
The emergence of modern means of information and communication has had a profound impact on social production and people's life. Modern tourist activity and the work of tourist firms cannot be imagined without the Internet. Modern audio-video technology has significantly changed management technology. Control is transferred to real time, etc.
Thus, innovative activity in the field of tourism is aimed at creating a new or changing an existing product, at improving transport, hotel and other services, developing new markets, introducing advanced information and telecommunication technologies and modern forms of organizational and management activities.
3. State support for innovative activities in tourism
Tourist activity is not only the provision of travel services, but also a source of income for the state and many sectors of its economy.
Tourism has a huge impact on such key sectors of the economy as transport, hotel and restaurant services, trade, construction, production of consumer goods and many others, acting as a catalyst for social and economic development.
Tourism is a complex cross-sectoral complex that requires a systematic approach to regulating the socio-economic interaction of many sectors of the economy at the state federal and regional levels.
The main tasks of the state are:
determination and development of the principles of tourism policy, programs for their implementation, a mechanism for monitoring and researching the results of activities (organization of statistics, departmental research);
creation of favorable conditions for tourism, coordination of actions of various companies, organizations and societies to form the appropriate infrastructure, friendly environment;
support for tourism and marketing by stimulating innovation and cooperation, creating an attractive image of the country.
Due to the fact that the creation and implementation of innovations require the combined efforts of various economic and social spheres, the innovative way of development is impossible without state support. For this, three schemes are used, which are also currently used in the development of the tourism sector.
Direct participation of the state in the implementation of special targeted programs and allocations of regional and local authorities; creation of large national centers (laboratories), funded by the budget and providing the acquired knowledge free of charge to a wide range of potential users.
Implementation of regional target programs in the field of tourism.
In many regions of Russia, regional target programs in the field of tourism are being developed and implemented, which, as a rule, include financing the following main activities: development of the tourism and transport infrastructure of the region, information promotion of tourism in the region, scientific and statistical research in the field of tourism, training and retraining of personnel for the sphere tourism. So, in the Vologda region since 2004 the regional target program "Great Ustyug is the homeland of Santa Claus" has been implemented, and in September 2008 a long-term target program "Development of domestic and inbound tourism in the Vologda region" for 2009-2012 was approved.
Creation of tourist information centers
Many states create special national organizations to promote various kinds of innovations in tourism. Finland is an example. The Finnish Tourist Board is a government agency that markets Finland as a tourism destination with offices in 11 countries. The Finnish Tourism Board was one of the first to use information technology in the work of the national tourism organization. It carries out strategic cooperation with representatives of the tourism industry and other interest groups, the overall goal of which is aimed at maximizing the country's presence and influence in the international market. Electronic information and communication technologies are the most important tools for achieving this goal. This council attaches particular importance to "creating a unique image of national tourism, clear segmentation of consumers and markets, effective marketing."
In Russia, there is no unified national organization for the promotion of the Russian tourist product, but tourist information centers (TIC) have been created and are functioning in many regions. As a rule, these are either state institutions or organizations in the form of non-profit partnerships, which are funded from regional or district budgets, can be regional, city or district.
State Institution "Tourist Information Center" of the Republic of Karelia. It has been operating since 2001, the founder is the Ministry of Economic Development of the Republic of Karelia. The tasks of ITC are: creation of a unified information bank of data on tourism potential, programs and projects on tourism in the Republic of Karelia; organization of information and consulting support on tourism activities, recreation in Karelia; promotion of Karelian tourist products, attraction of extra-budgetary funds for the development of tourism in the republic. ITC is a modern Internet technology that enables a potential tourist to receive comprehensive information on issues of interest to him about the possibilities of the tourist infrastructure of the Republic of Karelia.
State Institution "Tourist Information Center of the Vologda Region". It has been operating since 2007, the founder is the Committee for Tourism of the Vologda Region. The objectives of the TIC: development of the tourist attractiveness of the Vologda region, popularization of the project "Veliky Ustyug - the homeland of Santa Claus" in the media and promotion of the region in the Russian and international tourist markets; Consolidation of advertising and information work of various participants in the travel market in order to provide information and reference, tourist and business services to visiting tourists, as well as conducting advertising and marketing activities; organization of work with enterprises of the hospitality industry, assistance in the development of small and medium-sized businesses in the field of tourism.
Providing subsidies and grants for the implementation of research and development in the field of tourism and related industries.
A grant is government support or incentives for research and development with finance, property or services.
For the acquisition of research and development results that can bring direct benefits to the state, a state contract is concluded. It gives the right to the state representative to control and adjust the progress of the development.
Thus, the long-term target program "Development of domestic and inbound tourism in the Vologda Oblast" for 2009-2012 provides funds for scientific research in the field of tourism in the amount of 1.5 million rubles.
Providing private enterprises and individuals with favorable conditions for scientific and technical development, as well as the development of investment opportunities. Private businesses investing in research and the acquisition of the equipment necessary for this, as well as in the development of the tourist infrastructure of the regions, are provided with various tax incentives, government loans and guarantees, as well as financing through the participation of the state in the share capital.
Currently, a striking example is the creation in Russia in 2007 of seven tourist and recreational zones: Krasnodar and Stavropol Territories, Kaliningrad Region, Altai Territory, Altai Republic, Irkutsk Region and the Republic of Buryatia. This event symbolized the beginning of a period of active government support for the tourism industry, elevated to the rank of "locomotives" for the development of regions, and subsequently the Russian economy as a whole.
A tourist and recreational zone (analogous to service zones or service zones in world practice) is a type of special economic zone created for the development and provision of services in the field of tourism. Tourist and recreational zones are not widespread, but for Russia this is completely unique. Therefore, the creation of a TRZ in Russia is innovative.
The creation of special economic zones of a tourist and recreational type in Russia is one of the main priorities in ensuring the dynamic development of the country's economy, transferring it to an innovative development model, in combining the efforts of the state and the business community. The SEZ mechanism has a number of advantages: tax incentives, lower administrative barriers, budgetary investments in infrastructure, and an image component. It creates opportunities for effective testing of new approaches in public administration.
The objectives of creating tourist and recreational zones are: increasing the competitiveness of tourist activities, the development of health resorts, the development of activities for the organization of treatment and prevention of diseases. In tourist and recreational zones, the development of deposits of mineral water, therapeutic mud and other natural healing resources can be carried out.
The state, implementing the mechanism of public-private partnership, undertakes to create the necessary engineering, transport and social infrastructure, and also provides a certain set of benefits and preferences for investors.
To stimulate the investment activity of residents of tourist and recreational zones, the following tax incentives are established:
* residents have the right to: apply a multiplying factor of 2 when calculating depreciation; transfer the loss of the previous tax period to the current year in full; to recognize R&D expenses (including those that did not give a positive result) in the reporting (tax) period in which they were incurred, in the amount of actual expenses; not to pay within 5 years the property tax from the moment it was put into operation and the land tax from the moment the ownership right arose;
* the constituent entities of the Russian Federation have the right to establish for residents a reduced rate of income tax to be credited to regional budgets, but not less than 13.5%, and other tax benefits.
In addition, a simplified administrative regime will operate in the zones (the principle of a “one-stop shop” when registering residents and the possibility of conducting inspection activities - SES, fire service, trade inspection, labor inspection, etc. - only within the framework of a planned comprehensive audit, a decision which will be adopted by the territorial body of RosSEZ) and preferential land use procedure.
These innovations in the Law of the Russian Federation "On Special Economic Zones" should be recognized as positive, taking into account how widely unique resort and recreational facilities are represented on the territory of Russia, the development of which is significantly hampered by insufficient budget funding and state support.
It is especially important to create zones of this type for small and medium-sized businesses, since the development of a tourist and recreational zone is associated with the expansion of the service sector, the operation of a large number of hotels, catering establishments, etc.
Thus, “points of growth” have been created on the territory of seven constituent entities of the Russian Federation, which in the future should have a stimulating effect on the development of business in the regions and the territory as a whole. At the same time, the creation of tourist and recreational zones not only carries a positive economic effect for the region in the form of a growing volume of investments and the cost of services provided, the introduction of advanced technologies and modern management methods, stimulating the development of territories with low industrial potential, but also has an important social significance due to an increase in the number of jobs and an increase in the professional education of the population. In addition, as the world experience shows, the territories adjacent to the zone also begin to develop more dynamically.
Conclusion
The tourism industry today is one of the most promising and profitable. Globally, it accounts for about 10% of world gross income, 8% of total world exports and 30-35% of world trade in services.
Tourism is constantly evolving despite various political, economic and social obstacles. The tourist business in many cases is the initiator and experimenter in the development and implementation of modern advanced technologies, constantly changes the forms and methods of offering and providing services, opens up and assimilates new opportunities.
Tourism workers deal with a variety of forms and methods of organizing recreation, travel, cultural leisure. The development of the tourism business is possible only through the introduction of new ideas, the improvement of the production processes of goods and services, and the expansion of their range.
In tourism, innovations of the most diverse nature are introduced every day under the influence of both scientific and technological progress and the intellectual development of mankind.
Tourism innovations sometimes occur completely unexpectedly and even unpredictably under the influence of events in society. Therefore, the study of innovative processes, the reasons for the emergence of innovations, the development of methods for their implementation is of significant and practical scientific interest.
The role of the state in the development of innovations in the field of tourism is also important, and the development and implementation of mechanisms for state support of these areas is relevant.
tourism innovative vacation travel
List of references
1. Malakhova N.N., Ushakov D.S. Innovation in tourism and service. - M .: ICC "Mart", Rostov n / a: Publishing center "Mart", 2008.-224s. ("Tourism and Service");
Novikov V.S. Innovations in tourism: textbook. A guide for students. higher. study. institutions / V.S. Novikov. - M .: Publishing Center "Academy", 2007. - 208 p .;
Sevastyanova S.A. Regional planning of tourism and hotel industry development: a tutorial / S.А. Sevastyanov. - M .: KNORUS, 2007. - 256 p.
Modern dictionary of foreign words. About 20,000 words. SPb: Russian language: Duet: Kometa, 1994.- 395 p.
Http://www.ticrk.ru - site of the Tourist Information Center of the Republic of Karelia;
Http://vologdatourinfo.ru - site of the Tourist Information Center of the Vologda Region.
Tutoring
Need help exploring a topic?
Our experts will advise or provide tutoring services on topics of interest to you.
Send a request with the indication of the topic right now to find out about the possibility of obtaining a consultation.
It should be noted that a large role in the development of modern cultural and educational tourism belongs to competent, professionally trained managers and, not least, tourism specialists should be good psychologists. It is such well-trained professionals who can deal with various innovations and innovations in the tourism business. The new quality of growth, which is called development, is a consequence of the innovative nature of entrepreneurship in various fields.
In a market economy, tourism organizations are all aware of the need to develop new products and services and the associated benefits. Determining the future profit from a new tourism product is the task of innovation management.
What is he like? This is a separate type of cultural, economic and entrepreneurial activity to achieve the goals of travel companies based on the effective organization of innovative processes. In addition, innovative management presupposes the real and competent use of all available resources and the obligatory introduction of new forms of work. The innovation manager will have to induce and unite a large number of organizations and people for renewal to create the necessary and sufficient economic conditions and incentives to achieve the goal of innovation. Management of innovation is, to a lesser extent, an art than a science, and always carries a tinge of managerial personality. Kovalev G. D. Fundamentals of Innovation Management. - M., 1999 .-- P. 6.
Innovation management is a combination of various functions (such as marketing, planning, organization, development control). The main tasks of innovation management are to study the state of the sphere of economic activity and economic systems implementing innovations; study of the very specifics of the innovation process. Zaitseva N.A. Management in socio-cultural service and tourism. - .. 2003. - P. 281. The forms of introduction of innovations can be different, experts subdivide them into evolutionary and radical. These include preserving and updating existing functions, regrouping the constituent parts of the system, changing the elements of the existing system. To change the concept and results of the system, for all these new transformations, of course, special, innovative strategies are needed. They are divided into the following main types:
1) an offensive strategy (focused on new market prospects, its essence is to be the first in the market, which requires high qualifications and organization, as well as competent marketing; this strategy is based not on one single innovation, but on a whole series of innovations );
2) defensive strategy (entering the market after preliminary marketing);
3) absorbing strategy (buying innovations from other companies of a similar profile);
4) creation of a new market (application of our own innovations);
5) intermediate strategy (filling your niche between various competitors);
6) robbery strategy (the use of other people's innovations);
7) attracting strategy (creating a staff of new highly professional specialists).
Thus, innovation is an object introduced into production as a result of marketing and discovery, qualitatively different from the previous analogue. Innovation in any industry, including tourism, is qualitatively different from innovations. Innovative changes in tourism create the internal energy of efficient growth. These changes upset the balance, but create the foundations for further development, the transition of the system to a new quality. Therefore, it is the professional introduction of innovations into life that is the development of a particular industry. Modern society development experts argue that none of the problems that businesses face today are more important and complex than the problem of innovation.
Innovation in tourism naturally affects the state of the entire industry as a whole. They change the following key characteristics of the industry:
1) the volume of production and sales (in this case, new travel brands);
2) the operating costs of the innovation firm;
3) the size of the created and operating property;
4) the number of specialists involved in the design and implementation of a new tourist product on the market;
5) the duration of the development and implementation of innovations for consumers.
The efficiency of a modern tourist product, the rate of its development is determined by innovative activity and the production of "market novelty" goods, which either satisfy a completely new need or significantly expand the range of consumers. The innovation process, i.e. the process of introducing new products into the tourism market, is characterized by:
1) the multiplicity and initial uncertainty of ways to achieve the goal and high risk;
2) the impossibility of detailed planning and focus on forecast estimates;
3) the need to overcome resistance both in the sphere of existing relations and the interests of the participants in the innovation process. Innovations are the main means of increasing the value of the subject and the real sector as a whole in our case - the tourism sector. The higher the potential for innovation, the higher the expected real profit.
There is even the science of innovation, which deals with the study and implementation of innovations. In its scientific direction, it relies on the dialectical doctrine of universal development. Any innovations first lead to the creation of crisis states, a way out of which can be found only with a professional attitude to all stages of the process of introducing a new tourist product.
Therefore, any tourism manager needs to know that it is during the selection of innovations that innovations can appear, completely new forms of work. When conducting research on innovations, the following principles must be observed, in accordance with Figure 1.1:
1) the principle of importance;
2) the principle of filling the existing vacuum;
3) the principle of replacing old developments;
4) the principle of minimum capital investment;
5) the principle of mandatory demand;
6) the principle of perspective and development opportunities. Zaitseva N.A. Management in socio-cultural service and tourism. - .. 2003. - S. 184.
The tourism marketing in question has its own specifics. It is a set of specific functions carried out by a travel company in order to expand the market for its tourism products and services. Tourism marketing is the sphere of activity of tourism organizations to develop new, more efficient types of tourist and excursion services, as well as to produce and sell them in order to make a profit based on improving the quality of tourism products and taking into account processes in the global tourism market. Travel marketing has three main goals:
1) preservation of the traditional market;
2) development and expansion of a new market;
3) a decrease in the influence of seasonality.
In the tourism business there is a conditional division into four seasons: the "peak" season (mainly the summer period and calendar holidays), the "high" season (this includes the "velvet season, spring tours)," the "low" season (vacation time in winter and autumn period) and "off" season (the rest of the winter time). So, the main task of tourism marketing is to bring the new product closer to the consumer, which is capable of at least partly resurrecting the "dead" season.
To competently conduct marketing research in the field of tourism, one should follow such a simple scheme: Consumer desire - market research - making a profit by introducing new forms and satisfying the desires of buyers.
After studying the tourist market with the help of marketing research, you should correctly plan the appearance and development of a new product.
This requires:
1) generation of ideas - a systematic search for new solutions;
2) professional assessment of a tourist product using marketing results;
3) economic analysis - forecasting the volume of sales, costs and profits, drawing up a business plan;
4) development of a tourist product - creation of a conditional layout of a new product;
5) conducting trial marketing - evaluating a new product in a true real market environment;
6) commercial implementation, determining where, to whom, how to correctly and effectively offer an innovative tourist product.
As for drawing up a business plan, in this case it is called an innovative project and is determined by three main elements:
1) the purpose of the development and implementation of the project;
2) a plan-calendar of all planned events;
3) sources of funds.
Based on these three elements, as well as taking into account the economic justification of innovations, a decision is made on the feasibility and their implementation. After properly conducted marketing, project development and implementation, that is, bringing it to the consumer, the social effectiveness of innovations should be assessed (how much they meet the needs of society). The social effectiveness of innovation in tourism can be viewed in two dimensions. On the scale of social significance, the expected socio-economic results are assessed as an increase in national wealth due to an increase in the level of goods produced. Innovation fosters intensive growth in stocks and reserves, which determine the sustainability of the industry, the continuity of operations, even in the "low" and "dead" tourist seasons, and employment of the population. The accumulation of such reserves definitely expands the possibilities for the development of social and cultural facilities, helps to preserve the unique historical and natural monuments of our country. In addition, employment of the population in the process of production and product introduction improves living standards. Innovation helps people meet the ever-growing need for new products and use their free time.
On the scale of a specific tourist company or cultural and service organization, the unity of its technical, intellectual and commercial capabilities is realized. With innovations, the nature and conditions of work change. The changes resulting from the implementation of a new tourist product determine the social value of innovations. Kovalev G. D. Fundamentals of Innovation Management. - M., 1999 .-- p. 87.
The innovation sphere (in this case, tourism) should ideally have a special innovative infrastructure (national parks, cultural, entertainment and leisure centers, modern hotels, hotels, country clubs, roads, transport, etc.).
All of the above is a kind of innovation process, that is, a set of scientific, production, financial, commercial and organizational activities carried out in a certain sequence, leading to innovation. A large place in the modern tourism market has software service - a comprehensive presentation of a certain set of services to the client, subordinated to one goal (acquaintance with new places or certain monuments of antiquity or nature, learning, self-expression, just satisfaction of curiosity) with the help of a well-organized journey. In connection with the ever-increasing competition in the market, most travel companies offer their clients a comprehensive service, that is, a certain set of planned services. These services include:
1) decent living;
2) well-organized leisure and entertainment;
3) varied food;
4) sports in the form of a specific program;
5) excursions excellent in form and content;
6) affordable and convenient transportation.
Such services are offered in a wide range of thematic areas. Tourism, like any other branch of the economy, has its own specific development factors affecting the development and implementation of a new tourist product. In total, two main groups of factors can be distinguished:
1) static (natural and climatic, geographical, cultural and historical);
2) dynamic (political, socio-demographic, financial and economic, material and technical).
In tourism, as in any other modern industry, there is a special market for innovations that is part of the general tourism market. The market for innovations is formed under conditions of uncertainty, which arises from the very nature of the innovation process, and its formation should be considered in connection with the development of entrepreneurship in the tourism sector. The market for innovations is related to the supply and demand of innovations, the scale of prices, coverage of demand by a set of innovations, etc. The effect of the introduction of the innovation is manifested not only in the economic, but also in the social sphere, where by increasing incomes, social needs are more fully satisfied and the standard of living improves. In general, the economic efficiency of innovation is determined by comparing economic profits with the costs that caused the result. In other words, the effectiveness of a new tourism product depends on how much profit it brings to its designers, minus the money spent on its implementation.
In order for new tourism products to reach the potential consumer better and faster, periodic tourism fairs are currently held - organized in a certain exposition of the tourism product. These exhibitions are indispensable for presenting various innovations. They do not impose a new tourist product, but only create an atmosphere of favorable attitude towards it through professional presentation. Exhibitions - presentations of regions occupy a large place at tourism fairs, sometimes occupying several stands for new information about routes and tours. The largest tourism fair in Russia is the Moscow International Travel and Tourism Exhibition. It is the largest and most important exhibition of the tourist profile in Russia, held annually since 1993 in Moscow, at the Expocentre. This fair is attended by Russian and foreign travel companies and organizations, educational institutions of tourist destinations, embassies, all kinds of mass media, editors of television programs. The Moscow exhibition has its own catalog, in fact, the main source of information about tourist organizations and enterprises in the regions of Russia and in other countries. And one more novelty in modern Russian tourism.
This is automation, or the creation of search databases. The TURY.ru system was created specifically for the close contact of potential clients with tour operators. A single information field has been created in which everyone can quickly solve their problems. On hundreds of Internet sites, tourists communicate with managers in live mode. The main task of comprehensive automation of all links in tourism is being solved. Thus, the main problem in modern tourism is being solved - operational interaction between all parties to the transaction. The "Correspondence" section is built into every application. In short, the client visits the website, chooses a tour, enters into direct contact with the tour operator, agrees on the details of the trip and its main conditions, and the deal is made. Each of the parties to the transaction gets the opportunity to communicate effectively Let's see how such a system works in Figure 1.2.
At present, networks of travel agencies are being created in our country, operating in full cooperation. The most famous agencies are Vetrov Rose and Academservice. Agencies belonging to a particular network are jointly engaged in a new network tourism business in tourism. In turn, network agencies are connected to the newly created unified tourism system in Russia. The most modern Russian tourist network is Kuda.ru. Firms included in this network create joint data banks on tourist routes in all possible directions, as well as a complete client base. In addition, they exchange mutually beneficial information on any issues related to the development of domestic and inbound tourism.
So, the development of Russian national tourism in modern society has three foundations, "three whales":
1) the goal is the necessary tourist resources (natural, architectural, archaeological);
2) the level of comfort - providing tourist resources (hotels, hotels, entertainment and cultural centers, museums, roads, transport);
3) activating factors - sufficient tourist resources - specialists who plan, design, research, execute, market and implement.
From the foregoing, it follows that the main goals of modern tourism are the introduction of new models for the development of a tourist product, the effective use of their human resources, an increase in the role of a person and local communities, regional and territorial bodies and tourist organizations, overcoming financial, economic and social difficulties, organizing new forms leisure activities, development of innovations and introduction of new forms of work in tourism, etc.
Innovations (innovations) are possible in all areas of human activity. Based on the multivariate possibilities, innovations differ in the scope of application, scale of distribution and in nature.
In terms of application, innovations are subdivided into scientific and technical, organizational and economic, socio-cultural and state-legal.
According to the scale of distribution, they distinguish between global, national, regional, sectoral and local (at the enterprise, in the company) innovations.
They can be evolutionary and radical in nature.
Evolutionary innovations occur continuously and for the most part are the result of ideas and proposals coming from the sphere of production, marketing, consumption. The process of evolutionary innovations is entirely subordinated to social needs, is formed by effective demand and is limited by the possibilities of the technological potential of the system within which it occurs. The frequency with which an innovation is launched depends on the accumulated experience and knowledge. As a result, the company's ability to obtain and analyze information about consumer preferences, perception of market signals increases, and the accumulated knowledge allows improving products and technologies through innovations.
Evolutionary innovations can be classified according to the subject of the application, the impact on the manufacturing process and the activities of companies, and the nature of the needs met. The traditional approach to the typology of innovations by subject of the application is their division into innovation-products and innovation-processes.
Product innovation - an innovation in the form of a fundamentally new or improved product, which is promoted in the form of a product to the market. Often, the introduction of a new product is associated with the development or creation of new markets.
Process innovation is a technical, production and management improvement that reduces the cost of manufacturing a product. A process innovation can turn into a product innovation if it is in demand in the market. There is also a service innovation associated with servicing the processes of using the product outside the enterprise (computer software).
Innovations that affect the production process and the activities of companies in the market include technological, production, economic, trade, social, legal, managerial and informational.
In the service sector, innovations are fundamentally new or significantly improved methods of their production and provision (service), which cannot be provided by the previous production methods. These are tourism, banking, consulting services, and other sectors with a focus on the latest information and communication technologies.
Quite often, companies resort to adaptive innovation, which is a reaction to innovations introduced by competitors, in order to adapt to a changed situation and ensure the company's survival. A special place is occupied by pseudo-innovations that do not lead to a change in the consumer characteristics of products, but imitate them.
In terms of the nature of the needs being met, innovations that create new needs and develop existing ones can be classified as innovations.
Innovation can not only preserve and improve the technological and market capabilities of firms, but also, oddly enough, destroy them. So-called architectural innovations sometimes require replacement of existing technologies and products, as well as market-consumer relationships. Innovations, which create new market niches for existing technologies and products, lead to the emergence of a different category of consumers and destroy established market relationships.
Radical innovation is not a reaction to market needs. They are primarily associated with science, scientific discoveries, breakthrough inventions that have a certain independence from social needs. The use of radical innovations means a break with previous trends, opens up a new general concept for further improvements. The demand for them is unpredictable due to the lack of sufficiently clear areas of their application at the time of their appearance. Basic innovations based on new knowledge about the nature of the material world are distinguished among the radical innovations. They are the basis for the formation of a new technological order and determine its structure. Their introduction is associated with large investments in the formation of new industries and areas of development. Therefore, in the first phases of mastering basic innovations, direct and indirect government support is required. The process of their implementation is lengthy and accompanied by significant risks. Radical innovation falls into several categories. First of all, these are systemic innovations that provide the emergence of other innovations - improving (incremental innovations). Through them, the spread of fundamentally new equipment and technology in various areas of production is ensured, which contributes to the introduction of basic innovations. Such innovations provide important technical improvements to products, technological processes.