How to check for a breakdown on the housing. How to check the heating element in a washing machine at home? How to measure the power of a heating element with a multimeter. How to check the heating element of a washing machine: with a multimeter, tester, without a device
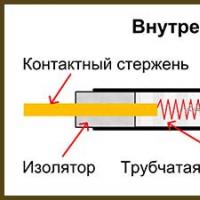
A tubular electric heater (TEH) is an electric heating element in the form of a metal tube of arbitrary shape, in which a spiral of nichrome or fechrome wire with leads at the ends is placed. To insulate the spiral and transfer heat from it, the tube is filled with quartz sand. The heating element has no polarity, so it does not matter to which terminal the phase and zero are connected.
Almost any modern electric heating devices, such as an electric kettle, an iron, an automatic washing machine, or a heater, use heating elements as a heat source.
If heating does not occur in an electrical appliance, this does not mean that the heating element has failed. It is quite possible that the cause of the malfunction could be a switch, thermostat or other controls. But usually the heating element is checked first, since checking it is not difficult. Any home master, having read this article, even without experience in checking and replacing heating elements, can easily cope with this task by choosing the most accessible method of checking.
Design of a tubular electric heater (TEH)
As can be seen from the drawing below, the heating element is a metal tube made of copper, stainless steel or iron, in the center of which there is a nichrome spiral, twisted in the form of a spring.

The tube inside is completely and tightly filled with sand, which allows you to effectively remove thermal energy from the spiral and prevent it from coming into contact with the tube. The ends of the spiral are connected by welding to contact rods, which are fixed inside the tube using ceramic insulators. To supply power voltage, threads are cut at the ends of the contact rods or contact plates are welded.
Tubes for the manufacture of heating elements are used in different diameters and, depending on the purpose, they are given different shapes, up to spiral-shaped. A good example is an electric boiler.
What are the types of heating element malfunctions?
Most often, heating elements fail due to the breakage of the nichrome spiral thread, which occurs due to the melting of the nichrome thread due to its overheating. Overheating occurs if a thick layer of scale has formed on the heating element or the heating element, designed to operate in a liquid environment, is turned on without it. The coil can burn out due to the initial low quality of the heating element.

The spiral in the center of the heating element tube is held in place by its dense filling with sand. If, when filling in sand, it was poorly compacted or the spiral moved from the center to the wall of the tube, then over time, due to vibration, the spiral may move and touch the inner surface of the tube.
If the spiral touches only at one point, then in the absence of connecting the grounding wire of the RCD in the apartment electrical wiring, the heating element will not lose its functionality and the electric kettle or any other heating device will continue to work. But in this case, there is a possibility of a phase getting into the body of the product, and if it is metal, then there is also the possibility of electric shock to a person when touching the body.

If the electrical appliance is grounded, then as a result of shortening the spiral, the released power will increase significantly and if the circuit breaker does not work, the spiral will melt and the heating element will fail completely.
If the spiral touches the tube in two or more places at the same time, as in the photo, then in the absence of grounding and an RCD, if the circuit breaker does not operate in time, the spiral will immediately burn out.
Thus, heating elements can have one of two malfunctions - a break in the nichrome spiral or a short circuit to the metal tubular shell. Any of these failures cannot be eliminated and the heating element must be replaced.
In modern electric kettles, multicookers and irons, heating elements are welded to the body of the product, and when the heating element fails, you have to buy a new electrical appliance.
How to check and ring the heating element
Depending on the availability of measuring instruments, you can check the heating element in one of the following ways. Measure the resistance of the spiral and the resistance between the spiral and the tube using a dial tester or multimeter, ring using a phase indicator or an electrician's control.
Checking the heating element
using a dial tester or multimeter
To check, you need to turn on the device in the minimum resistance measurement mode and touch the leads of the heating element with the ends of the probes of the device.

If the spiral is broken, then the pointer tester will show a resistance equal to infinity, and the multimeter will show “1” instead of the real resistance, which is equivalent to infinite resistance.
It is enough to enter into the calculator windows the voltage for which the heating element is designed and its power. Typically these values are embossed on the tube. You can use information about the power consumption of an electrical appliance. For example, the resistance of the heating element of an electric kettle with a power of 2000 W will be 24.2 Ohms.

If the spiral is intact, then you need to touch any of the heating element terminals with one end of the multimeter probe, and the metal tube with the other. If there is no short circuit between the spiral and the tube, then the dial tester will show infinite resistance, and the multimeter will show “1”. If the device shows a value different from the specified value, then a short circuit is evident and such a heating element is not subject to further operation.
Checking the heating element
using LED and battery or power source
If you don’t have a tester or multimeter, or the Krona-type battery in the multimeter is dead, then if you have any LED, and they are in almost all household electrical appliances, and any battery, even a dead one, with a voltage from 3 V to 12 V, you can successfully check any heating element, including an electric kettle.

In the photo you see how you can use a dead Krona battery removed from the multimeter (the voltage at its terminals was only 5 V instead of 9 V), a 51 Ohm resistor and an LED to check the integrity of the heating element coil. Just remember that the LED is not a light bulb and must be connected with correct polarity. Since the heating element itself has a resistance, when checking the coil using an old battery, you can do without a resistor.
If the LED lights up, it means the spiral is intact. To check the insulation resistance, you need to disconnect the circuit from any of the contact rods of the heating element and touch the heating element tube. The LED should not light up.

If you don’t have a battery on hand, you can successfully replace it with any AC or DC power source; any charger, for example, from a cell phone or laptop, will also work. In this photo, power is supplied from a DC source using alligator clips. The LED shone confidently when the voltage changed from 2.5 to 12 V.
Checking the heating element using a phase indicator
Attention! When checking the heating element using a phase indicator and electrician control, care should be taken. Touching exposed parts of a circuit connected to an electrical outlet may result in electric shock. In other words, touching the body of the heating element and its terminals with your hand after connecting to the outlet is unacceptable.
If you have an electrician’s phase indicator on hand, you can also use it to check the serviceability of the heating element. In this case, the insulation resistance (between the nichrome spiral and the tube) will be checked with greater reliability, since when checking with a multimeter, a voltage of no more than 9 V is applied, and when checking with an indicator, more than 220 V.

To check, you must first determine where the phase is located in the socket (according to the rules it should be on the right) and then connect one of the contact rods of the heating element with a piece of wire to the phase terminal, as shown in the photo.
If, when you touch the opposite terminal of the heating element, the indicator light does not light up, it means that the spiral is broken, and if it lights up when you touch the tube, it means that there is an insulation breakdown (the spiral touches the tube).
Checking the heating element using an electrician's control
Almost anyone can check the heating element using an electrician’s control, since no measuring instruments are required. The essence of the test is to connect any light bulb in series with the heating element spiral, followed by connecting the circuit to 220 V household wiring.
To prepare for the test, you need to take a plug with a cord and connect one end of it to any contact terminal of the heating element, and the other end to the electric cartridge. Next, an additional piece of wire is connected to the second terminal of the cartridge. Any light bulb rated for 220 V is screwed into the socket.

First, the free wire from the socket is connected to the free end of the heating element, as shown in the diagram above. The plug is then inserted into the socket. If the spiral is working properly, the light bulb should shine brightly. If there is no light, then the spiral is broken and you don’t have to check it further, since the heating element is not subject to further use.

Next, the plug is removed from the socket and the right terminal from the socket according to the diagram is connected to the heating element tube, as shown in the photo. The plug is inserted into the socket; if the light does not light, it means that the insulation resistance between the spiral and the tube is high and the heating element is working. If the light bulb starts to glow, then there is an insulation breakdown and it is unacceptable to operate such a heating element.
Non-standard ways to check heating elements
If it is not possible to check the heating element using one of the above methods, then you can connect the wires from the cord with a plug directly to the terminals of the heating element and insert the plug into the socket for a few seconds. If the heating element starts to heat up, then the coil is intact. Be careful not to get burned with your hand when checking the heating temperature of the heating element.
To check the insulation resistance, one of the ends of the cord, with the plug removed from the socket, must be disconnected from the heating element output and connected through a fuse designed for a protection current of no more than 5 A to the heating element tube. Then insert the plug into a household electrical outlet. There is no time limit here. If the fuse does not blow immediately, then there is no short circuit between the coil and the housing and the heating element is working.
It is simply unrealistic to list all possible ways to check the heating element. The heating element can even be checked using a landline telephone by connecting it to a break in one of the wires with which the phone is connected to the network. If after connection there is a signal in the removed tube, then the heating element is working. You can even not pick up the phone, but call him from your mobile phone. The presence of a bell sound will confirm the integrity of the heating element coil.
Visual inspection
If you do not have a multimeter, then the performance of the part can be checked by visual inspection.
First way. The wash should be started. And start watching your electric meter, in particular the wheel. If it picks up speed, then most likely the heating element is working.
Second way. Visual inspection. Remove the heating element. To do this, you need to unscrew the nut that is located in the middle. Next, you need to press on the end of the protruding bolt so that it goes deeper, and pry off the heating element with a knife. Now that we have the heating element in our hands, we can carefully examine it from all sides. If you find even minor cracks or black spots on the part, then most likely it is faulty.

Please take note
- When you install a new heating element or return the old one to its place, carefully ensure that all connections are absolutely tight. Make sure that the heating element is in the correct mount located at the bottom of the tank. Otherwise, the part will touch the drum during washing. Which, of course, will not have a very good effect on its future performance.
- Do not neglect preventive measures that will help extend the life of the heating element. Once every six months, run the wash in the standard cycle with an empty drum. Instead of washing powder, add a spoon or two of citric acid. This method will remove scale formed during operation. Read more about methods of dealing with scale on heating elements.

Conclusion
If your washing machine has stopped heating water, do not rush to buy a new one. Perhaps the problem lies simply in a faulty heating element. The part should be dismantled and ringed to confirm or exclude the guess that it is the heating element of the washing machine that is damaged.
If this manipulation does not reveal the malfunction, then a careful inspection of the heating element will help to fully verify its functionality. If the defect is confirmed, the electric heater must be replaced. A new part can be ordered through the service center.
Almost all heating devices and instruments known today function thanks to the operation of tubular electric heating elements, which are briefly called heating elements. As a rule, heating elements are distinguished by their simple design and long service life, however, if used incorrectly or if they are defective, they fail - the most common causes of device malfunctions are spiral rupture and short circuit.
Before throwing away faulty equipment, it is recommended to check the heating element using a multimeter. Perhaps the problem is not in this part at all, and the breakdown is much more serious. So, how to check the heating element using an ordinary tester?
A tubular electric heating element contains one or more spirals that have high resistance, due to which they heat up when electric current passes through them. To avoid short circuits and other electrical problems, the coils are placed in insulated metal tubes.
Before checking the heating element, it is necessary to determine its normal resistance. This is necessary so that when testing you have a standard with which to compare the readings of the device. This way you can easily determine how much the value measured by the multimeter differs from the calculated one, and how much these values diverge.
R=U 2 /P
Where P– power indicated on the equipment casing. So, if an electrical device operates under a voltage of 220 Volts, and its power is 1000 Watts, the resistance calculated by the formula will be equal to 48.4 Ohms. As you can see, calculating the value is very simple!
Checking an ordinary heating element
Now that you know how to determine the resistance of a heating element and why it needs to be done, you can proceed directly to the testing itself, which is performed in several steps.
Before checking the heating element with a multimeter, disconnect the heating element from the power supply.
In further actions, follow the instructions below for correct verification:

- The resistance is equal to the calculated one - the device is serviceable and suitable for use.
- The display shows the value 0 – short circuit of the spiral inside the tube.
- The display shows the value 1 (or infinity) – a break in the heating coil.
After completing the verification procedure, it is necessary to engage in ringing, which allows you to determine whether an electrical breakdown occurs on the device body. Dialing is also carried out using a tester as follows:

If, at the moment the probes touch the contacts, the buzzer begins to emit high-frequency signals, then an electrical breakdown occurs on the device body, which can lead to electric shock with serious consequences for health and life.
Checking the heating element of the water heater
If until now you did not know how to check the heating element of a water heater with a multimeter, good news for you - it is practically no different from the previously discussed example and is not difficult even for inexperienced users. The procedure for testing is completely similar to that described above, since the design of heating elements in different equipment is practically no different. The only addition is that it is recommended to check the thermostat.
In the normal case, when testing a water heater heating element, the tester shows the resistance value, which in most cases takes values of 0.37 and 0.71.
It is also necessary to check the element for a breakdown on the device body. You already know how to ring a heating element with a multimeter - this was discussed above. Switch the tester to buzzer mode and touch the contacts one by one, listening to the signals emitted by the multimeter.
Checking the heating element of the washing machine
Before you check the heating element of a washing machine with a multimeter, you still need to find it - many people have certain difficulties with this, which is especially true for modern machine models with tricky internal structures. In most cases, the heater in the washing machine is located slightly below its tank, closer to the back cover.
 On some models it is installed on the front cover side. Top-loading washing machines can be equipped with elements located on one of the sides.
On some models it is installed on the front cover side. Top-loading washing machines can be equipped with elements located on one of the sides.
When checking, you should know which contacts of the heating element you need to connect to. The fact is that the tubular electric heating element of the washing machine has three outputs, of which only two are needed for testing. As a rule, the grounding contact is located in the center, while the two outermost ones (zero and phase) are the terminals necessary for checking.
 To test the heating element of the washing machine, you must follow the instructions given earlier. The normal resistance value for the heating element of a standard washing machine varies between 25-60 Ohms, small deviations are possible.
To test the heating element of the washing machine, you must follow the instructions given earlier. The normal resistance value for the heating element of a standard washing machine varies between 25-60 Ohms, small deviations are possible.
Sometimes there is a breakdown inside some household appliance that is simply impossible to notice and see. It happens that the water heater works as before, but diagnostics still won’t hurt. Therefore, in this situation, verification with various methods and instruments will be required. It is necessary to check the water heater, since the boiler is a complex system consisting not only of electrical functions, but it is also aimed at working with water. Water and electric current are a complex combination, so any malfunctions can lead to disastrous results.
Water heater inside
Checking the heating element of a water heater using a tester
There are a large number of ways. The most commonly used method is in which the test is carried out using a special tester. Before checking, you need to calculate the resistance for the installed boiler.
Formula for calculation: R=U*U/P, where:
- U - This is a constant value, equal to 220 volts.
- P - This is the power of the device; you can find it in the boiler’s instruction manual or on the factory sticker, which is located at the bottom of the boiler or on the back side.
Using a Multimeter
The multimeter has a flag that you can rotate 360 degrees and select to test any function. It needs to be turned to measure a resistance of 200 ohms. The multimeter contacts should be connected to the heating element connection. If the water heater rings, that is, it is completely working, then the same value will appear on the screen as was previously calculated using the formula.
If the display shows zero, one or an infinity sign, then this indicates some kind of breakdown, for example, a short circuit or break. In this case, you will have to change the part; repair will not work.
![]()
Failure of the heating element
Next, you need to check the boiler itself for a breakdown of the casing, this is even easier to do. The flag must be turned until the buzzer rings. The first contact of the multimeter must be connected to the tubular electric heater, and the second to the shell of the water heater or the ground terminal.
If the multimeter starts to beep, this indicates a breakdown of the housing, so in this case you should absolutely not touch the boiler itself, as an electric shock may occur, not fatal, but quite strong.
Application of a megohmmeter
Its flag must be turned towards 50 volts, one contact must be connected to the heating element contact, and the second to the body. If a value of more than 0.5 Mohm appears on the megohmmeter display, then the water heater is fully operational.
RCD for water heater
An RCD is a special device that helps protect a water heater from current leaks. The RCD looks like a small box with two lights and one button.
The operating principle is as follows:
- The RCD is installed directly in front of the water heater itself; all the electric current passes through the RCD, which powers the boiler mechanism.
- As soon as a current leak occurs inside the boiler, which can become life-threatening, the RCD will detect the leak and turn off the entire system. The RCD operates using special sensors and switches.
![]()
What does an RCD look like?
Reasons for disconnecting the RCD:
- Incorrect location of the RCD. If the RCD is connected in the wrong place, then the system will conduct through itself the wrong electric current that is needed, so in the event of a breakdown, the system will not be able to protect a person from current leakage.
- The insulation of the heating element is damaged. This function protects the entire system from the passage of current through water. In old or unknown cheap models, this element can be damaged, so even with normal hand washing a person can receive an electric shock.
- Leakage current. A common reason for tripping the RCD is a broken cable or any other wire inside the boiler. In frequent cases, the cable is damaged from the inside, so the current is transferred to the boiler body, and since it is metal, the shock can be very strong when touched. In this case, you will have to check it from the inside.
It is important to install the RCD correctly, because it is what saves you from fires, explosions and other various situations that can harm others.
Checking the water heater thermostat
You can check the thermostat using a multimeter.
The check is carried out as follows:
- The multimeter flag must be turned to resistance measurement mode.
- Next, you should connect the contacts of the multimeter to the contacts of the thermostat.
![]()
Correct connection of the multimeter
- If an infinite value appears on the multimeter display, the thermostat will have to be completely replaced; it cannot be repaired.
- If resistance appears on the display, then you should set the checkbox to a lower value, and then warm up the thermostat pipe with a lighter; if it works properly, the resistance will increase sharply and a protective reaction will occur.
Checking the water heater safety valve
The safety valve is an important part in the operation of the water heater.
![]()
Safety valve
You can check the operation of the safety valve as follows:
- First, you need to make sure that the hot water supply tap is not opened until the water is heated to its maximum. If the valve is working properly, excess water should begin to drip through it.
- If water does not drip from the valve, then most likely it is faulty and will have to be replaced.
Do not proceed with replacement without checking the hot water tap. It should not leak, since excess water can leak through it, and therefore the valve will not work.
The valve may not work if the thermostat is installed incorrectly, namely for incomplete heating of the water, and also if water is drawn from the water heater, which reduces the pressure in it.
Checking the heating element of a water heater without a tester
To check the heating element without a tester, you will need another device, namely an electrician’s test lamp, which you can make yourself by finding instructions or video tutorials on the Internet.
![]()
DIY control lamp
One of the contacts of the heating element must be supplied with zero from the network, and the second contact with phase through the same lamp. If the light comes on, then the heating element is working properly and there is nothing to worry about.
Checking the water heater thermostat
A water heater thermostat is a device that regulates the heating of the boiler and controls the water temperature. In simpler terms, a thermostat is needed to heat running water to a certain temperature, and then automatically turns off and also automatically turns on when the water has cooled to a certain temperature and needs to be heated again.
You can check the thermostat as follows:
- First you need to remove the thermostat and find out if it is working. It needs to be switched to resistance measurement mode.
![]()
Water heater thermostat
- Then you need to set the maximum temperature and measure the resistance at the thermostat output and input contacts. The thermostat is broken and malfunctioning if the system does not respond at all.
- If the thermostat is working and the system has responded, then the regulator flag must be set to the lowest value and the tester contacts must be connected to the boiler contacts.
- Finally, you need to heat the tubular element of the thermostat using a lighter. If the system turns out to be working, the resistance indicator will increase greatly.
To check the thermostat you will need a multimeter, which was used in the first case; it is very functional.
![]()
Multimeter
Conclusion
Routine water heater inspections are essential to avoid disastrous results such as electric shock, water heater bursting, neighborhood flooding, and more. In everyday life, every person needs to have a multimeter, since all tests are carried out with its help. If, during the inspection, any malfunctions were noticed, then you should not do the repairs yourself; you should call a specialist who will help solve the problem.
To connect plumbing fixtures to the water supply network, a flexible water supply is used. It is in demand when connecting faucets, showers, toilets and other water intake points, and significantly simplifies the installation process. Flexible connections are also used when installing gas equipment. It differs from similar water devices in its manufacturing technology and special safety requirements.
Characteristics and types
The flexible hose for connecting plumbing is a hose of different lengths made of non-toxic synthetic rubber. Thanks to the elasticity and softness of the material, it easily takes the desired position and allows installation in hard-to-reach places. To protect the flexible hose, there is an upper reinforcing layer in the form of a braid, which is made from the following materials:
- Aluminum. Such models can withstand no more than +80 °C and retain functionality for 3 years. At high humidity, aluminum braiding is prone to rust.
- Of stainless steel. Thanks to this reinforcing layer, the service life of the flexible water line is at least 10 years, and the maximum temperature of the transported medium is +95 °C.
- Nylon. This braid is used for the manufacture of reinforced models that can withstand temperatures up to +110 °C and are designed for intensive use for 15 years.
The fasteners used are nut-nut and nut-fitting pairs, which are made of brass or stainless steel. Devices with different permissible temperatures differ in the color of the braid. Blue ones are used for connecting to a pipeline with cold water, and red ones for connecting to hot water.
When choosing a water line, you need to pay attention to its elasticity, reliability of fasteners and purpose. It is also mandatory to have a certificate that prevents the rubber from releasing toxic components during operation.
Features of gas connections
When connecting gas stoves, water heaters and other types of equipment, flexible hoses are also used. Unlike water models, they are yellow and are not tested for environmental safety. For fixation, end steel or aluminum reinforcement is used. There are the following types of devices for connecting gas appliances:
- PVC hoses reinforced with polyester thread;
- made of synthetic rubber with stainless steel braid;
- bellows, made in the form of a corrugated stainless steel tube.

The Santekhkomplekt holding offers engineering equipment, fittings, plumbing fixtures and devices for connecting them to communications. The assortment is represented by products and materials from well-known foreign and domestic manufacturers. Discounts apply for bulk purchases, and product quality is confirmed by standard certificates. For information support and assistance, each client is assigned a personal manager. The ability to arrange delivery within Moscow and to other regions of the Russian Federation allows you to quickly receive the purchased goods without unnecessary hassle.
Drainage is a drainage and drainage measure to remove excess groundwater.
If water does not leave the site for a long time, the soil becomes gleyed, if shrubs and trees quickly disappear (get wet), you need to urgently take action and drain the site.

Causes of soil waterlogging
There are several reasons for soil waterlogging:
- clay heavy soil structure with poor water permeability;
- aquifer in the form of gray-green and red-brown clays is located close to the surface;
- high groundwater table;
- technogenic factors (construction of roads, pipelines, various objects) that interfere with natural drainage;
- disruption of the water balance by the construction of irrigation systems;
- The landscape area is located in a lowland, ravine, or hollow. In this case, precipitation and the influx of water from higher places play a big role.
What are the consequences of excess moisture in the soil?
You can see the results of this phenomenon yourself - trees and shrubs die. Why is this happening?
- the oxygen content in the soil decreases and the carbon dioxide content increases, which leads to disruption of air exchange processes, water regime and nutritional regime in the soil;
- oxygen starvation of the root-forming layer occurs, which leads to the death of plant roots;
- the supply of macro and microelements by plants (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, etc.) is disrupted, because excess water washes out mobile forms of elements from the soil, and they become unavailable for absorption;
- intensive breakdown of proteins occurs and, accordingly, the processes of decay are activated.
Plants can tell you at what level groundwater lies
Take a close look at the flora of your area. The species inhabiting it will tell you at what depth the ground water layers are located:
- perched water - it is best to dig a reservoir in this place;
- at a depth of up to 0.5 m - marigold, horsetails, varieties of sedges grow - bladderwrack, holly, foxweed, Langsdorff's reed;
- at a depth of 0.5 m to 1 m - meadowsweet, canary grass, ;
- from 1 m to 1.5 m – favorable conditions for meadow fescue, bluegrass, mouse peas, rank;
- from 1.5 m - wheatgrass, clover, wormwood, plantain.
What is important to know when planning site drainage
Each group of plants has its own moisture needs:
- with a groundwater depth of 0.5 to 1 m, vegetables and annual flowers can grow in high beds;
- depth of water layer up to 1.5 m is well tolerated by vegetables, grains, annuals and perennials (flowers), ornamental and fruit shrubs, trees on a dwarf rootstock;
- if the groundwater is more than 2 m deep, fruit trees can be grown;
- The optimal depth of groundwater for agriculture is from 3.5 m.
Is site drainage necessary?
Record your observations for at least some time. You yourself can understand how much drainage is needed.
Maybe it makes sense to simply redirect melt and sediment water along the bypass channel, rather than allowing it to flow through your site?
Perhaps it is necessary to design and equip a storm drain and improve the composition of the soil and this will be enough?
Or is it worth making a drainage system only for fruit and ornamental trees?
A specialist will give you the exact answer, and we strongly recommend calling him. But after reading this article, you will gain some awareness on this issue.
Upon completion of the technological and production tasks associated with the arrangement of a sewer system in an apartment building, industrial building, as well as in a private household, it is necessary to test the involved system using the forced flow method. This task is used to identify possible defects or improper installation of the entire involved sewerage part, and the test report for internal sewerage and drainage systems will be material evidence of the work on acceptance of the facility.

A visual inspection should be accompanied by inclusion in the test report of internal sewerage and drainage systems according to SNIP, which is currently represented by the current regulations of the “D” series appendix, which corresponds to SP 73.13330.2012 “Internal sanitary systems of a building”, recently a new one has been applied updated working edition according to SNiP 3.05.01-85.